|
| ←2026→| Months |
|---|
| Jan |
Feb | Mar |
| Apr |
May |
Jun |
| Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
| Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
Thu, Jan 07, 2016 11:58 pm
VBScript - List Installed Programs
I had been
using
InstalledPrograms.vbs, a
VBScript script written by
Bill James,
to query systems for a list of installed programs. I ran the script today
while logged into a user's account on a Microsoft Windows 7 system, I received
an error message because the script was in a sudirectory beneath
C:\Program Files and the script's output file is stored by
default in the directory from which the script is run, but the user's account
did not have permission to write to that directory. To fix the problem,
rather than move the script to another directory or run the script from
an administrator account, I added VBScript code from Rob van der Woude's
Browse Folder Dialog function so that a user can select the
directory to be used for the output file.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/vbs]
permanent link
Sun, Sep 25, 2011 9:25 pm
List Installed Programs
I needed to produce a list of programs installed on a Microsoft Windows system
to send to someone else so she could check it for no longer
needed programs and tell me which ones are no longer needed, so I could
remove them to free disk space. Bill James has a
VBScript script,
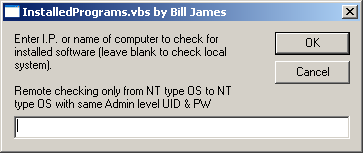
InstalledPrograms.vbs, which can be run from a command line,
which prompts for the name of the system to check via a popup window,
as shown below:
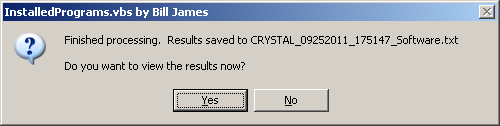
After that prompt, you are asked whether you wish to view the results
produced by the program as shown below.
The list of installed programs is stored in a file that
has the name of the system on which it is run followed by
an underline, then the date in mmddyyyy (month-date-year)
format, then another underscore followed by the time in military
time, i.e. 24-hour clock time, another underscore and then
"Software.txt". E.g. CRYSTAL_09252011_175147_Software.txt
for a file produced when the program was run on a system named Crystal
on September 25, 2011 at 5:51:47 PM. The file is stored in the directory
in which the script is run.
If you click on "yes" to view the results, the file produced by the program
will be opened in the default .txt file viewer, which, on Microsoft Windows
systems, will likely be Notepad.
An example output file can be seen
here.
The list is similar to the list of installed programs that you would see
by checking with "Add or Remove Programs" under the Control Panel.
It is obtained by querying the registry key
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\.
Download InstalledPrograms
References:
-
VBScript Tools by Bill James
BillsWay.com
-
VBScript
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
[/languages/vbs]
permanent link
Fri, Oct 10, 2008 11:45 pm
Querying the Dell Service Tag with VBS
I needed to produce a list of the service tags for all of the Dell
systems at a site. I found a Visual Basic script at
Query Dell Service Tag that could query a Dell system for the service
tag. There were two versions there, one that would request the system
name through a pop up window and another that could be run from a command
prompt.
I wanted to be able to run such queries from a command prompt, so the
second version appealed to me. But it only queried one system at a time,
so I modified the script to allow me to specify multiple systems at one time
on the command line. The updated script is available at
Dell-ServiceTag.vbs.
Usage:
cscript /nologo Dell-ServiceTag.vbs a b c
Output:
Computer: a Dell Service Tag: AGXQVD1
Computer: b Dell Service Tag: BRKF462
Computer: c Dell Service Tag: 1NFWLB3
[/languages/vbs]
permanent link
Mon, Nov 12, 2007 9:02 pm
Silent Runners
Silent Runners is a Visual
Basic script, which can be used to scan a system for software that
starts automatically when Windows starts, which may aid you in determining
if a system is infected with malware.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/vbs]
permanent link
Sat, Sep 22, 2007 11:59 am
Visual Basic Script to Check CPU Utilization
A user of a Windows 2000 Professional system was complaining that his system
has been running very slow. He has stated that when he is typing in a Word
document or an email message that the time between when he types characters
and when they appear on his screen can be quite lengthy. I've seen problems
on his system before with high CPU utilization and wanted to use a script
that would monitor and record CPU utilization on his system.
I found a script posted on TechRepublic at
CPU Utilization Script1.
I modified the script so that I could
specify the time interval between CPU utilization checks through an argument
to the script when it is run. The modified script is available at
CPU_Use.vbs
2.
The script can be run with csript /nologo CPU_Use.vbs or
alternatively cscript /nologo CPU_Use num where "num" is the
number of seconds to wait between CPU checks, e.g. csript /nologo CPU_Use
300 to check every 5 minutes.
The output is placed in C:\Processor.log; the output location can
be changed by modifying the value of the strLogFile
variable in the script. Output will look similar to the following:
9/22/2007 09:43
9/22/2007 09:48 19
9/22/2007 09:53 17
9/22/2007 09:58 17
9/22/2007 10:03 35
9/22/2007 10:08 14
9/22/2007 10:13 15
The first two columns list the date and time the script was run while
the third lists the CPU utilization at the time the script was executed.
There is no value for CPU utilization for the first entry in the log.
The script requires Windows XP or later. It will not run on Windows 2000.
If it is run on Windows 2000, you will see
CPU_Use.vbs(48, 1) Microsoft VBScript runtime error: ActiveX component
can't create object: 'WbemScripting.Swbemrefresher'
3, 4
Most of the systems I support are Windows XP systems, so the script will
still be useful to me, but I can't check the system I wanted to check
in this case, since that system is a Windows 2000 system.
References:
-
CPU Utilization Script
By: neilb
Posted: January 4, 2006
TechRepublic
-
CPU_Use.vbs
By: Jim Cameron (modifications to script written by neilb)
MoonPoint Support
-
ActiveX component can't create object: 'WbemScripting.Swbemrefresh
Posted By: Daniel
Date: April 19, 2005
Ureader.com - Microsoft community
-
SWbemRefresher Object
Microsoft Developer Network
[/languages/vbs]
permanent link
Fri, Jan 12, 2007 9:48 pm
Who is Logged On to a Computer - VBS Script
If you need to know whether anyone is logged into a remote computer
in your domain or who that might be, you can use
LoggedOn.vbs,
a script I found at
List User Logged On To A Remote Computer, which was written by
Cheyenne Harden and is available at the
LazyNetworkAdmin.Com website
or from this site (see links below).
To use the utility, you can enter LoggedOn.vbs
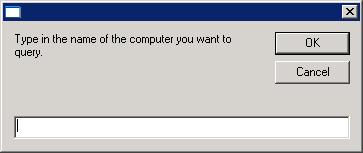
at the command line while in the directory where the file
is located. A small window will open prompting you for the name
of the computer to query.
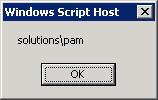
You will see the logged on user displayed in a small Windows
Script Host window as shown below:
If no one is logged on to the system, you will see "null" displayed
in the small Windows Script Host window that opens.
If you want the logged on user information displayed in a form
that you can copy and paste into a document, you can use
cscript /nologo LoggedOn instead. The results will
then be displayed on the command line as below:
C:\Program Files\Utilities\Miscellaneous>cscript /nologo LoggedOn.vbs
solutions\pam
If no one is logged into the system, you will see "null" displayed
on the command line.
C:\Program Files\Utilities\Miscellaneous>cscript /nologo LoggedOn.vbs
null
If the system can't be queried, you won't see an error message.
Instead, you won't see anything displayed.
Information on other utilities to display the logged on user can
be found at Who Is
Logged On?.
LoggedOn.vbs
LoggedOn.zip
References:
-
List User Logged On To A Remote Computer
By Cheyenne Harden
LazyNetworkAdmin.com
-
Who Is Logged On?
MoonPoint Support
[/languages/vbs/sysadmin]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 10, 2006 11:15 pm
Who Is Logged On?
If you need to determine who is logged into a Windows system, there are several
alternatives for collecting that information from a command line interface. One
of method is to use a
Visual Basic
script to determine who is logged on, such as the
WhoLogon.vbs
script by
Guy Thomas.
Or you can use the free
PsLoggedOn utility by Mark Russinovich at
Sysinternals.
There is also a whoami utility within the
Native Win32 ports of some GNU utilities, which contains ports of some
common GNU utilities to native Win32.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/vbs/sysadmin]
permanent link
Thu, Aug 04, 2005 8:20 pm
Prnmngr.Vbs
Microsoft provides a prnmngr.vbs script with Windows XP and Small Business
Server (SBS) 2003 systems. This script can be found in %windir%\system32,
which will normally be c:\windows\system32. The script can be used to add,
delete, and list printers or printer connections. It can also be used to
set or display the default printer. If you run the script using cscript without
any parameters it will display the usage information shown below. If you are
unfamiliar with cscript, it provides a mechanism for running VBS scripts. The "/nologo" option
for cscript supresses the display of the Microsoft logo information normally
displayed when a script is run with cscript. You can run the script from
a command line. You need to change to the %windir%\system32 directory or
include the full path to the script when you run it, e.g.
cscript /nologo c:\windows\system32\prnmngr.vbs -l.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>cscript /nologo prnmngr.vbs
Usage: prnmngr [-adxgtl?][c] [-s server][-p printer][-m driver model]
[-r port][-u user name][-w password]
Arguments:
-a - add local printer
-ac - add printer connection
-d - delete printer
-g - get the default printer
-l - list printers
-m - driver model
-p - printer name
-r - port name
-s - server name
-t - set the default printer
-u - user name
-w - password
-x - delete all printers
-? - display command usage
Examples:
prnmngr -a -p "printer" -m "driver" -r "lpt1:"
prnmngr -d -p "printer" -s server
prnmngr -ac -p "\\server\printer"
prnmngr -d -p "\\server\printer"
prnmngr -x -s server
prnmngr -l -s server
prnmngr -g
prnmngr -t -p "\\server\printer"
If you want to view the default printer for a system you can use the
-g parameter.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>cscript /nologo prnmngr.vbs -g
The default printer is Microsoft Office Document Image Writer
If you want to view all of the printers for a system and save the
output to a file, such as printers.txt, you could use the following command.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>cscript /nologo
c:\windows\system32\prnmngr.vbs -l >printers.txt
The information that will be displayed for each printer when you use the
-l option will be similar to that shown below.
Server name
Printer name HP Business Inkjet 3000 PCL 6
Share name Pam HP3000
Driver name HP Business Inkjet 3000 PCL 6
Port name USB002
Comment
Location
Print processor WinPrint
Data type RAW
Parameters
Attributes 8776
Priority 1
Default priority 0
Status Unknown
Average pages per minute 0
References:
-
Microsoft Windows XP - Prnmngr.vbs"
-
Handy VBS Scripts
[/languages/vbs]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact







