←March→
| Sun |
Mon |
Tue |
Wed |
Thu |
Fri |
Sat |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
| 8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
| 15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
| 22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
| 29 |
30 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tue, Mar 03, 2026 3:33 pm
Adding the capability to save webpages as a single file to Firefox
The Firefox web
browser does not have the capability to save the contents of a webpage to a
single file, such as an
MHTML file, which is
a web archive file format that allows one to save the
HTML code, images
etc. on a webpage into a single file.
Though the capability is absent from Firefox, you can add the functionality
of saving a page to a single file by installing
Save
Page WE, an
add-on for Firefox
by DW-dev. The
extension provides the capability to "Save a complete web page (as
currently displayed) as a single HTML file that can be opened in any browser.
Save a single page, multiple selected pages or a list of page URLs. Automate
saving from command line." The saved file is not an MHTML file,
or one of the other common
web
archiving file formats, but it
is a single HTML file that Firefox and other browsers can read.
Save Page WE is implemented using the
WebExtensions API and is available for both Firefox and
Chrome with
identical functions and user interfaces.
When you start the installation process, you will see a list of the
permissions required by the extension:
- Access your data for all websites
- Download files and read and modify the browser's download history
- Display notifications to you
- Access browser tabs
- Access browser activity during navigation
Click on the Add button to add the extension. You should then
see the message "Save Page WE was added. Update permissions and data preferences any time in the extension settings." You also have the option to pin the
extension to the toolbar.
Select the option to pin the extension to the toolbar, which will
result in an icon of a 3.5" floppy disk appearing on the toolbar.
You can click on that icon to save the page displayed in the current
browser tab.
You can also save a page by hitting the Alt+A key
combination (you can cancel the saving of a page with At+C).
The file format is HTML rather than MHTML, so the
file extension
used by SavePageWE is .html, which Firefox can open — if you try to open
a file with the .mhtml extension, Firefox will prompt you to use another
application to open the file.
Anyone who wishes to have the ability to save a webpage as a single file
added to Firefox, can add their voice to the post at
Add native Web Archive File support to Firefox, including MHTML, MAFF, and
Webarchive...
References
-
How to save a webpage as .mhtml with Firefox?
Last updated: September 15, 2024
superuser
-
Add native Web Archive File support to Firefox, including MHTML, MAFF, and
Webarchive...
Date: August 15, 2023
By:
JohnBoyTheGreat
moz://a Connect
[ More Info ]
[/network/web/browser/firefox/addons]
permanent link
Mon, Mar 02, 2026 11:11 pm
Turning off Fast Startup on a system running Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows 8 introduced a feature called
Fast Startup. The feature was a variation of hibernate mode, but when
enabled would close all running programs and log the user out before
hibernating. This feature would result in a user being able to log in
more quickly when a system is powered back on after a shutdown. There may
be cases where use of this feature is not desirable, however. E.g., if the
user wants to boot the system into
Linux, but still access data
on the Windows boot drive. To turn fast startup off, you can take the
following steps:
-
Type
Control Panel in the Windows Search field
at the bottom of the screen.
-
Click on System and Security.
-
Click on Change what the power buttons do under Power
Options.
-
Click on Change settings that are currently unavailable.
If prompted for administrator credentials, provide those for
an administrator account.
-
Uncheck the check box next to "Turn on fast startup (recommended)".
-
Click on Save changes. You can then close the window.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows]
permanent link
Sun, Mar 01, 2026 10:55 pm
Controlling whether a scrollbar appears in a tab in a Terminal window
I needed to scroll back through a tab I had open in a
Terminal window on
an
Ubuntu Linux system,
but there was no
scrollbar on the right side of the tab in which I had run the command,
though a scrollbar was open in other Terminal tabs. I was able to get the
scrollbar to appear by clicking on the icon with 3 horizontal bars at
the top of the Terminal window and then selecting
Preferences.
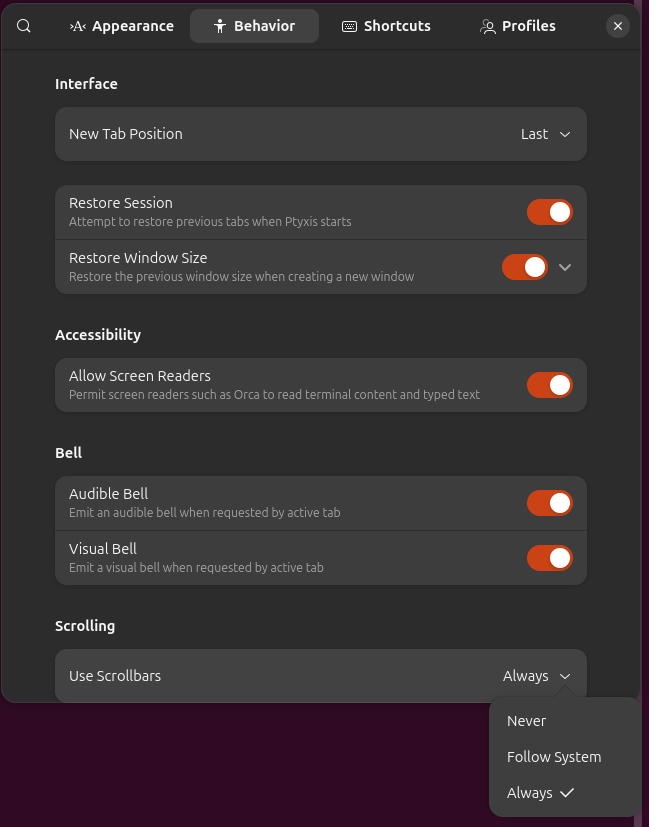
Then from the Behavior tab, I changed the setting from
Follow System to Always, which resulted in the
scrollbar appearing where it had been missing, but I could not scroll
back any further than the text that had been appearing in the tab
before I changed the settiing and that remained the same whenever
I issued another command and text moved upwards, so that I could no
longer see it or scroll back to see it, so I closed the tab.
When I opened another tab, the scrollbar was there and operated
as expected.
[/os/unix/linux/ubuntu]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 28, 2026 8:29 pm
Creating a desktop shortcut under Ubuntu for a Windows app runnning under Wine
From a CD, I
installed
Microsoft Office 2007 under
Wine, so that
my wife could edit her
Microsoft
Publisher files on an
Ubuntu Linux system. I also installed
Microsoft Excel
and Microsoft Word.
All three seemed to be working OK when I checked them after the
installation completed. I was able to open the programs from the
File Explorer by
issuing the command wine explorer from a
shell prompt in
a Terminal window
and then navigating to the directory,
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Office12, where the
applications were located. I could also start Publisher by issuing the command
below in a Terminal window:
wine "/home/alice@Wonderland/.wine/drive_c/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft Office/Office12/MSPUB.EXE"
To make it easer for my wife to open Publisher, though, I created a
shortcut on her Ubuntu desktop. To create a shortcut you can take the
following steps:
Open a Terminal
window and create a new .desktop file on your desktop. You can use
the nano
editor or another text
editor to create the file. E.g., nano
~/Desktop/AppName.desktop.
You then need to have lines like the following ones in the file:
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Name of Your Application
Exec=wine "/home/username/.wine/drive_c/Program Files/AppName/app.exe"
Type=Application
Icon=wine
Terminal=false
StartupNotify=true
You need to use the absolute path the the .exe file for the program and,
if the directory
path contains a space, you must enclose the path within quotes. Also,
you need to replace username with your username on the system.
For Publisher, I could use the following lines:
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Publisher
Exec=wine "/home/alice@Wonderland/.wine/drive_c/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft Office/Office12/MSPUB.EXE"
Type=Application
Icon=wine
Terminal=false
StartupNotify=true
If you use the nano text editor, you can hit Ctrl+X, the
Y, then Enter to save the file. You then need to make
the shortcut executable, which you can do by right-clicking on the file
on the desktop, selecting Properties, and then makng sure "Executable
as Program" is on. Or you can use the
chmod command to make
the file excutable by a command like chmod +x ~/Desktop/AppName.desktop
. You then need to permit launching of the application from the shortcut
by right-clicking on it and selecting Allow Launching.
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/linux/wine]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 27, 2026 3:41 pm
Wine window becoming transparent with an attempt to resize it
My wife was using Advanced Diary for
journaling on a Microsoft Windows system, but wanted to transition to
Linux, so I installed
Ubuntu Linux and then,
since there is no Linux version of Advanced Diary, I installed
Advanced Diary under
Wine. She wanted to adjust the size of the Advanced Diary window, but when
she attempted to adjust the window size by clicking on the
Restore Down icon at the top right side of the
window (between the dash and the "X"), the Advanced Diary window became
transparent and it was not possible to close it or adjust the size of the
transparent box that appeared for the Advanced Diary window.
So I had to open a
Terminal window to determine the
process ID (PID)
of the Advanced Diary process with the
ps and then kill that
process with the
kill command. I could also have used the
killall command
killall AdvancedDiary.exe.
I tried closing and opening the program several times. The behavior
was consistent — the window would become transparent whenever
I tried resizing or minimizing the window.
If you are using the
GNOME desktop, you can use the steps below to try to resolve the problem.
GNOME is the default desktop environment for Ubuntu, but you can verify
it is the desktop in use by the command echo $XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP.
Steps that may resolve the problem:
-
Run winecfg in a Terminal window.
-
In the Wine configuration window, click on the Graphics
tab.
-
Toggle the settings for "Allow the window manager to decorate the windows"
and "Allow the window manager to control the windows" one by one to see if
one of those settings change the behavior. When I toggled off "Allow the
window manager to decorate the windows", I now no longer saw the icons
to adjust the size of the window or minimize the window at the top of the
Wine window for Advanced Diary, but when I clicked where I expected them
to appear, the window became transparent again. I toggled the setting back
on and then toggled off the "Allow the window manager to control the
windows" setting. That resolved the problem. I then closed the window
and reopened Advanced Diary and toggled that setting on again, also, so
that both settings were checked. I could still adjust the window size
as expected. I closed and reopened the application several times
and was still able to adjust the window size, so just toggling the
"Allow the window manager to control the windows" setting off and
then back on seemed to resolve the problem.
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/linux/wine]
permanent link
Thu, Feb 26, 2026 10:31 pm
Restarting the Windows audio service
If you are experiencing problems with sound on a Microsoft Windows system,
such as being unable to hear audio even when the sound hasn't been muted
and any external speakers are turned on and set to an audible volume level,
one possible way to resolve the problem is to restart the
Windows Audio service. To do so, you can can take the following steps:
- Type
services in
the Windows Search field. You should see it returned by the search
utility. Click on "Run as administrator" and provide the login credentials
for an account that has adminisrator privileges.
- When the Services window opens, scroll
down until you see Windows Audio.
- Right-click on the entry and choose "Restart".
- When the status for the service returns to "Running",
you can close the Services window.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows]
permanent link
Wed, Feb 25, 2026 11:57 pm
Configuring Sendmail to listen on the mail submission port
Sendmail is an
email server application that is available for many operating systems.
It will listen on
TCP
port 25 for connections from other mail servers that use the
Simple
Mail Transfer Protocol for email transmissions. As
a message
submission agent (MSA), another common port it listens on is TCP port 587
for email transmissions from users' email clients. On a
Linux system you can use the
netstat or
ss
commands to determine if a system is listening for connections on a
particular port. When I checked a Sendmail server to determine whether it
was listening on port 587, I could see that it was not listening on that
port, though that was needed.
# netstat -an | grep 587
# ss -ln | grep ":587 "
#
When I searched /etc/mail/sendmail.mc for
RELAY_MAILER_ARGS, I saw the following
lines, which are needed to have Sendmail listen for email transmissions
from users on TCP port 587, were already present and were not commented out:
define(`RELAY_MAILER_ARGS', `TCP $h 587')
define(`ESMTP_MAILER_ARGS', `TCP $h 587')
When I searched for DAEMON_OPTIONS, I saw the following:
dnl # The following causes sendmail to additionally listen to port 587 for
dnl # mail from MUAs that authenticate. Roaming users who can't reach their
dnl # preferred sendmail daemon due to port 25 being blocked or redirected find
dnl # this useful.
dnl #
dnl DAEMON_OPTIONS(`Port=submission, Name=MSA, M=Ea')dnl
I removed the dnl from the begining of the line so that
I then had the line below, instead:
DAEMON_OPTIONS(`Port=submission, Name=MSA, M=Ea')dnl
I then rebuilt /etc/sendmail/mc and restarted the Sendmail
service.
# m4 /etc/mail/sendmail.mc > /etc/mail/sendmail.cf
# service sendmail restart
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart sendmail.service
#
I could then see that the system was listening for connections on port
587.
[ More Info ]
[/network/email/sendmail]
permanent link
Tue, Feb 24, 2026 4:06 pm
Installing Advanced Diary on a Linux system with Wine
I needed to install Advanced Diary
on an Ubuntu Linux system.
for someone who had been using the program for journaling on a Microsoft Windows
system. I had previously installed
Wine, a program that
allows one to run Windows applications on
Linux,
macOS, and
FreeBSD
systems. I used AdvDiary.sh, which
contains the following lines, to install Advanced Diary:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -e
if [ -z "$1" ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 AdvancedDiarySetup.exe"
exit 1
fi
INSTALLER="$(realpath "$1")"
PREFIX="$HOME/.wine-advdiary"
echo "Creating 32-bit Wine prefix..."
export WINEPREFIX="$PREFIX"
export WINEARCH=win32
winecfg -v win7 >/dev/null 2>&1 || true
echo "Installing required components (gdiplus, corefonts)..."
winetricks -q gdiplus corefonts
echo "Forcing native GDI+..."
cat > "$PREFIX/user.reg" <<'EOF'
[Software\\Wine\\DllOverrides]
"gdiplus"="native"
EOF
echo "Running Advanced Diary installer..."
wine "$INSTALLER"
echo
echo "✔ Installation complete"
echo "Run with:"
echo "WINEPREFIX=$PREFIX wine \"$PREFIX/drive_c/Program Files/Advanced Diary/Diary.exe\""
To run it, you need to assign "execute" permission to the file, which can be
done in a Terminal
window with chmod + x filename or chmod a+x
filename to make a file executable by all users or
chmod u+x filename to make it executable by just the owner
of the file, i.e., the user.
alice@Wonderland:~/Downloads$ chmod u+x install-advanced-diary.sh
alice@Wonderland:~/Downloads$
When I ran the shell
script .sh file, I realized I hadn't installed
Winetricks beforehand, so I installed it with
sudo apt install winetricks after running the script.
I then reran the installation script for Advanced Diary. The installation
completed successfully — I selected the option to have the program
opened automatically at the conclusion of the installation — and it
appeared to open normally (I had to press Enter in the terminal
window to return to the shell prompt).
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/linux/wine]
permanent link
Mon, Feb 23, 2026 10:05 pm
Determining if a drive is encrypted with Bitlocker on a Windows system
If you need to determine if a drive in a Microsoft Windows system or connected
to it via USB is
BitLocker encrypted, you
can use the
manage-bde utility. To use the program, open a
command prompt window with
administrator privileges and then issue the command
manage-bde -status to see the status of all drives. To see just
the status of one drive, e.g., C:, you could use manage-bde -status
C:.
C:\Windows\System32>manage-bde -status c:
BitLocker Drive Encryption: Configuration Tool version 10.0.26100
Copyright (C) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Volume C: [Windows]
[OS Volume]
Size: 14826.87 GB
BitLocker Version: None
Conversion Status: Fully Decrypted
Percentage Encrypted: 0.0%
Encryption Method: None
Protection Status: Protection Off
Lock Status: Unlocked
Identification Field: None
Key Protectors: None Found
C:\Windows\System32>
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/commands]
permanent link
Sun, Feb 22, 2026 3:38 pm
Running the Big Fish Games Manager on an Ubuntu system
You can run the Big
Fish Games Game Manager on an
Ubuntu Linux system
under Steam.
You can install Steam as a
Snap package
from the Ubuntu App Center.
Steps:
-
Download the Big Fish Games App (Game Manager) for PC
-
In Steam on the Ubuntu system, click on Add a Game, which is
at the lower, left-hand corner of the Steam window, then
select Add a Non-Steam Game, then browse to where you downloaded
the .exe installer for the game manager, click on it, and then
click on Add Selected Programs.
-
You should then see the Big Fish Game Manager in the "Uncategorized" list
of games at the left side of the Steam window, e.g., you may see
bfginstaller32_s1_l1.exe listed. Right-click on it and then select
Properties, then Compatibility, and then, from the
drop-down list that becomes available, select Proton Experimental
or the latest stable version — I selected Proton Experimental.
-
You can then close the Compatibility window by clicking on the
"X" at the upper, right-hand corner.
-
Then with the Big Fish Game Manager selected in the Uncategorized
list, click on the Play button to launch the Big Fish Game Manager
Setup and agree to the License Agreement when you see it appear.
When I started the install process, the installation appeared to hang at
"Execute: C:\Program Files (x86)\bfglient\epoch.exe". When I clicked on the
title bar for the window, I saw "About Wine", so it appeared to be using
Wine, which I had
previously installed on the Ubuntu system.
But I waited and eventually the installation succeeded, though I think it
took over 15 minutes. I closed the window and then went back to the
Steam window, I saw bfginstaller32_s1_l1.exe was still there. This time
when I clicked on it, the Big Fish window where I could sign in to Big
Fish Games opened fairly quickly.
Note: if the window goes blank or displays just a white background,
minimize it by clicking on the "-" in the upper, right-hand corner of
the Big Fish window and then switch to it again, which you can do with
Alt+Tab — continue to press the Tab key while
continuing to hold down the Alt key to cycle between open open
windows until you get to the Big Fish window.
Initially, you will see "No games to play," but if you have already
purchased games that you've played on another system, you can click
on Purchase History and install them on the Linux system.
When I installed the Big Fish Games Manager under Steam, I had my wife
check one of her games, Aquascapes, and that ran fine. I then closed
the Big Fish window and the Steam window and reopened it. Note: if
you want to change the name that appears for Big Fish Games in the
Uncategorized list, you can right-click on the entry, e.g.,
bfginstaller32_s1_l1.exe, and choose Properties and then change
the "Shortcut" value to something you prefer, such as "Big Fish Games".
When I reopened Steam and started Big Fish Games, I saw the Aquascapes
game under "My Games".
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/linux/ubuntu]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact




