Enabling DNS Logging on a Windows SBS 2003 Server
Domain Name System (DNS)
logging can be used to monitor what other systems a particular system
is contacting, which may be important information when you are trying to
determine what is happening with a system infected with malware. By enabling
DNS logging, you can see not only what systems are being contacted, provided
the infected system looks up an IP address from a name rather than having
hardcoded IP addresses it contacts, but when it was trying to contact those
systems.
To turn on DNS logging for a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for Small Business
Server, which is functioning as a DNS server, take the following steps:
- Click on the Start button.
- Select Administrative Tools.
- Select DNS.
- Right-click on the DNS server and select
Properties.
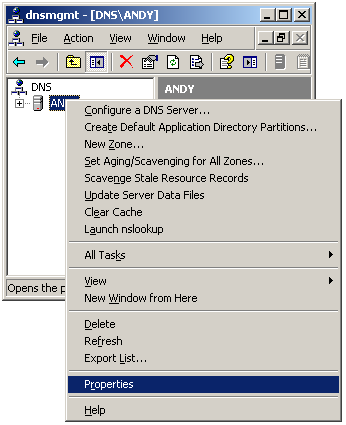
- Click on the Debug Logging tab.
- Check the box next to Log packets for
debugging. Ensure that at least Incoming, UDP,
Queries/Transfers, and the packet type of Request are
checked. You may also want to log TCP packets, outgoing packets, and
response packets as well to see the IP addresses returned by the DNS
server for queries on names.
Specify the directory path and file name for the log file. You can
also specify a maximum size, if you wish. The default value is
500,000,000 bytes, i.e., 500 MB. If you only want to log DNS queries
and responses coming from and/or going to a particular IP address,
you can check the box for "Filter packets by IP address" and then click
on the Filter button to specify the IP addresses.
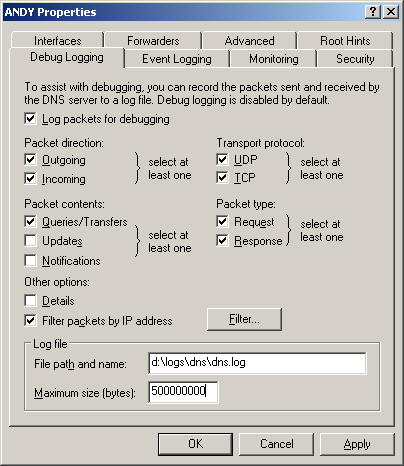
- Click on OK.
- If you don't want to see any other entries in the log,
e.g., for problems on the DNS server, you can click on the Event Logging
tab and set the value for "Log the following events" to "No events"
and click on OK.
If you wish to delete an existing log file that is in use and start a
new one, right-click on the DNS server in the dnsmgmt window, select
All Tasks, then Stop. You can then move or delete
the log file, right-click on the DNS server again, select All Tasks,
then Start to restart logging.
When You check the log file, entries will appear in the following format:
20141119 20:42:13 158C PACKET 01D02360 UDP Snd 192.168.0.15 7033 R Q [8081 DR NOERROR] A (5)loadr(8)exelator(3)com(0)
In the above example, the system at IP address 192.168.0.15 requested the IP
address for loadr.exelator.com.
A valuable and free tool which can aid you in examining Microsoft Windows
DNS log files is Windows
DNS Log Analyser.

Created: November 19, 2014



