←July→
| Sun |
Mon |
Tue |
Wed |
Thu |
Fri |
Sat |
| |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
| 6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
| 13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
| 20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
| 27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
Thu, Jul 31, 2014 10:48 pm
Uninstalling Shoutbox on an SMF 2.0.x forum
Since I had replaced Shoutbox on a
Simple Machines Forum (SMF) site running
SMF 2.0.8 with
CometChat,
I was asked to uninstall the Shoutbox mod and delete the files associated
with it from the site.
SMFPacks Shoutbox 1.0.3 was shown in the packages list, but there was
no option to install or uninstall it, only options to "List Files" or
"Delete". But there was a configuration page for it within the forum
software. That page showed that Shoutbox was disabled.
I found in the Packages directory for the forum there was a
SMFPacks_Shoutbox.zip file. When I unzipped the file and
checked the package-info.xml for it, I saw the following
in the installation section for 1.x versions of SMF:
<!-- 1.1.x -->
<install for="1.1-1.1.99">
There was an installation section for 2.0.x versions of SMF as well:
<!-- 2.0.x -->
<install for="2.0">
Since it did not list a range of version numbers, I went to Admin, then
Package Manager and then clicked on the Advanced link at
the bottom of the list of mods. I then changed the Emulate Version value
from 2.0.8 to 2.0 and clicked on the Apply button. I was then able to
uninstall SMFPacks Shoutbox 1.0.3 and delete the files associated with
it. I then clicked on the Advanced link again at the bottom of the list
of mods, clicked on Revert beneath Emulate Version, and then
clicked on the Apply button to put Emulate Version back to
its original value.
[/network/web/forums/smf]
permanent link
Sun, Jul 27, 2014 5:30 pm
Copying a MySQL table from one database to another
To copy a MySQL table, both the structure and data, from one database to
another, the following two commands can be used inside MySQL where
db1 is the original database and
db2 is the
new database and
table is the name of the particular table
you wish to copy.
CREATE TABLE db2.table LIKE db1.table;
INSERT INTO db2.table SELECT * FROM db1.table;
[/software/database/mysql]
permanent link
Sun, Jul 27, 2014 4:30 pm
Showing all MySQL databases or all tables in a database
For MySQL on a Linux system, if you need a list of all MySQL databases
you can display a list of the databases by logging into MySQL and
then issuing the command
show tables; or from a shell
prompt you can issue the command
mysqlshow -u username -p
where
username is a MySQL username. The
-p option will
result in a prompt for the password associated with the username.
$ mysqlshow -u jdoe -p
Enter password:
+--------------------+
| Databases |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| jdoedbf |
| test |
| tokyo |
+--------------------+
If you need a list of all tables in a MySQL database, you can display a
list of tables by logging into MySQL with an account that has access
to the database and then issuing the command
show tables;
or from a shell prompt you can issue the command
mysqlshow -u
username -p dbname where
username
is the account with access to the database and
dbname is
the name of the database. The
-p option will prompt for
the password for the account.
$ mysqlshow -u jdoe -p products
If you need to find a table with particular text in the name, you can
pipe the output of the mysqlshow command into grep. E.g., if you were looking
for a table in a database named "products" with many tables that contained
"cat" as part of the name of the table, you could use something like
the following:
$ mysqlshow -u jdoe -p products | grep cat
[/software/database/mysql]
permanent link
Sat, Jul 19, 2014 5:17 pm
Taking a screenshot with scrot
Scrot is a command line
screen capturing application for Linux systems developed by Tom Gilbert.
If the package is installed, you can type
scrot
imagefile to take a snapshot of the screen and store it in
the file named
imagefile, e.g.,
scrot test.png. If you
don't want the terminal window from which you ran the command captured in
the screenshot, you can issue the
sleep command followed by
some delay in seconds followed by a semicolon and then the scrot command
to give you time to minimize the terminal window from which you ran the
command. E.g.:
$ sleep 10; scrot test.png
The above command would give you 10 seconds to minimize the terminal
window and any other open windows you didn't want to see in the screenshot.
The results of the screenshot would be stored in the directory from which
the command was run in the file test.png. Or you can use
the scrot command's own delay parameter, -d or --delay
followed by the number of seconds of delay you wish to give yourself
before scrot captures the screen, e.g., scrot -d 10.
For help on the utility issue the command scrot --help.
scrot --help
Usage : scrot [OPTIONS]... [FILE]
Where FILE is the target file for the screenshot.
If FILE is not specified, a date-stamped file will be dropped in the
current directory.
See man scrot for more details
-h, --help display this help and exit
-v, --version output version information and exit
-b, --border When selecting a window, grab wm border too
-c, --count show a countdown before taking the shot
-d, --delay NUM wait NUM seconds before taking a shot
-e, --exec APP run APP on the resulting screenshot
-q, --quality NUM Image quality (1-100) high value means
high size, low compression. Default: 75.
For lossless compression formats, like png,
low quality means high compression.
-m, --multidisp For multiple heads, grab shot from each
and join them together.
-s, --select interactively choose a window or rectangle
with the mouse
-u, --focused use the currently focused window
-t, --thumb NUM generate thumbnail too. NUM is the percentage
of the original size for the thumbnail to be,
or the geometry in percent, e.g. 50x60 or 80x20.
-z, --silent Prevent beeping
SPECIAL STRINGS
Both the --exec and filename parameters can take format specifiers
that are expanded by scrot when encountered.
There are two types of format specifier. Characters preceded by a '%'
are interpreted by strftime(2). See man strftime for examples.
These options may be used to refer to the current date and time.
The second kind are internal to scrot and are prefixed by '$'
The following specifiers are recognised:
$f image path/filename (ignored when used in the filename)
$m thumbnail path/filename
$n image name (ignored when used in the filename)
$s image size (bytes) (ignored when used in the filename)
$p image pixel size
$w image width
$h image height
$t image format
$$ prints a literal '$'
\n prints a newline (ignored when used in the filename)
Example:
scrot '%Y-%m-%d_$wx$h_scrot.png' -e 'mv $f ~/images/shots/'
Creates a file called something like 2000-10-30_2560x1024_scrot.png
and moves it to your images directory.
This program is free software see the file COPYING for licensing info.
Copyright Tom Gilbert 2000
Email bugs to <scrot_sucks@linuxbrit.co.uk>You can also type man scrot to see information on use
of the utility.
References:
-
Scrot
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
-
The Tom Gilbert Blog
[/os/unix/linux/utilities/graphics]
permanent link
Sat, Jul 19, 2014 1:11 pm
Steps for taking a screenshot in GIMP
Steps for taking a screenshot in
GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP), which
is a free graphics program available for Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, and
Microsoft Windows systems.
- Click on File.
- Select Create.
- Select Screenshot.
- When the GIMP screenshot window opens, you will have the option of
selecting the area for the screenshot.
Area
- Take a screenshot of a single window
[ ] Include window decoration
- Take a screenshot of the entire screen
[ ] Include mouse pointer
- Select a region to grab
Delay
[ 0 ] seconds
At the end of the delay, click in a window to snap it.
- When you have selected the option you want, click on the
Snap button.
If you choose to take a screenshot of a single window, the cursor will
change to something similar to a "+". Move the cursor over the appropriate
window and that window will be pasted into a GIMP window when you click on the
window. Note: make sure you don't have any windows overlapping the one
you wish to capture, otherwise you may see a portion of an overlapping
window in the screenshot.
If you don't want to capture the border around a window, scrollbars for
the window, and any application menu at the top of the window, uncheck
"Include window decoration.
If you choose "Take a screenshot of the entire screen", a snapshot
will be taken of the entire screen including the GIMP window.
If you select a region to grab, the cursor will change as above. You can
then click in one corner of the area of the screen you wish to include in
the snapshot then drag the mouse to a diagonal corner while holding the
mouse button down. When you release the button, the area selected will
be captured.
Once you have the screen shot, you can create a GIF, JPG, PNG, etc. image
file from the screenshot by clicking on File and selecting
Export.
[/software/graphics/gimp]
permanent link
Fri, Jul 18, 2014 8:53 pm
Determining the default browser from the command line
If you need to determine the default browser on a system running
Microsoft Windows, you can look in the registry at
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\http\shell\open\command
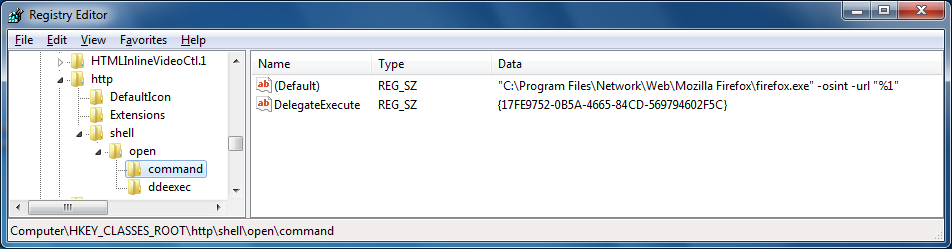
To determine the default browser from the command line, you can use
the command reg query HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\http\shell\open\command
/ve.
C:\>reg query HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\http\shell\open\command /ve
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\http\shell\open\command
(Default) REG_SZ "C:\Program Files\Network\Web\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe" -osint -url "%1"If you just wanted a true or false result for determining whether Firefox
is the default browser, you could pipe the output of the reg query
command to the find command as below. A result of 0 means "false", i.e.,
Firefox is not the default browser and a result of 1 means it is the default
browser.
C:\>reg query HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\http\shell\open\command /ve | find /c /i "firefox"
1
Reference:
-
How Does Your Browser Know that It’s Not The Default?
Date: March 23, 2007
The New Old Thing | Absurdity in Its Fullest
[/network/web/browser]
permanent link
Tue, Jul 08, 2014 10:57 pm
Junos Pulse VPN Client Issue on Mac OS X
The Junos Pulse 5.0.3 VPN client had been working fine on my Mac OS X laptop
for quite some time, but recently whenever I opened it, it would show
"Disconnecting". I could click on the
Connect button, which
resulted in the application displaying "connect requested", but the
application would never connect nor disconnect. I could select
"Close Junos Pulse" in the application, but when I restarted the
application I was in the same situation. I could probably have resolved the
problem by rebooting, but since I had a lot of applications and files open
and didn't want to have to close all the files and applications, I looked for
another alternative. Issuing the following commands at a command prompt
from a terminal window allowed me to eliminate the problem without rebooting.
$ launchctl unload -w /Library/LaunchAgents/net.juniper.pulsetray.plist
$ sudo launchctl unload -w /Library/LaunchDaemons/net.juniper.AccessService.plist
Password:
$ osascript -e 'tell application "Junos Pulse" to quit'
The account I was logged in under had adminisrator level access, so I
simply provided its password at the password prompt above.
When I reopened Junos Pulse afterwards, it wasn't showing any available
connections, so I closed it and then issued the commands below.
$ sudo launchctl load -w /Library/LaunchDaemons/net.juniper.AccessService.plist
$ launchctl load -w /Library/LaunchAgents/net.juniper.pulsetray.plist
When I then reopened the Junos Pulse application through the Finder,
I saw the VPN connection I normally use and was able to successfully
establish a VPN connection. And I was able to disconnect without a
problem afterwards.
[/os/os-x]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact



