I installed copSSH 1.4.6 on a Windows Vista Ultimate system. The software is an implementation of an SSH server and client for Windows systems. I had been using OpenSSH for Windows 3.8.1p1 on Windows 2000 and XP systems, but I haven't been able to get it to work under Windows Vista. I haven't had any problems getting copSSH to function as an SSH server under Vista.
At the end of the installation, the installation software displays the message below:
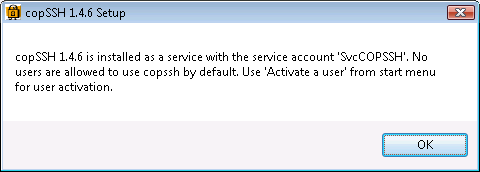
After the installation, I clicked on Start, selected All Programs, then COPSSH, then Activate a User.
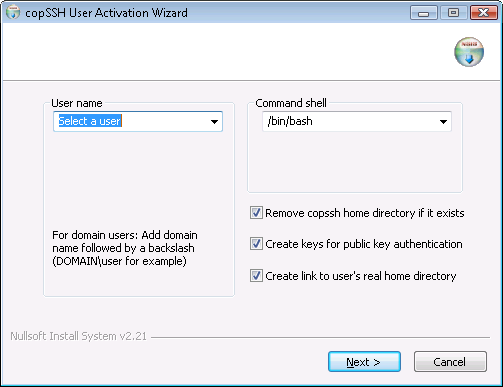
I selected a user and then proceeded to the next step where I typed in a passphrase, which is used to protect the private key for the account.
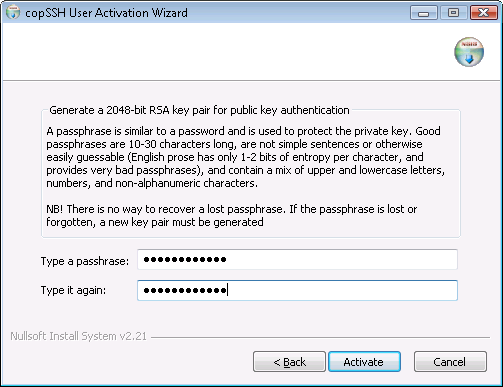
I then clicked on the Activate button, which produced the message below.
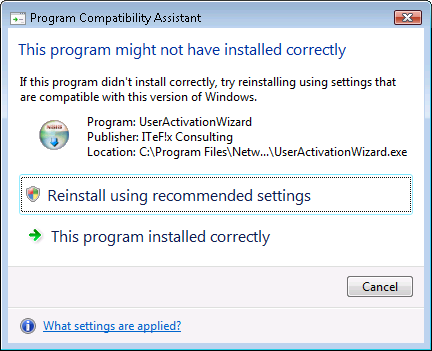
I selected the "This program installed correctly" option.
Since the system was using the firewall capability built into Windows Vista, I then clicked on the Start button, selected Control Panel, then Security then Windows Firewall, and then Change Settings.
I clicked on the Exceptions tab and then selected Add Port.
At the Add Port window, I specified copSSH as the name
for the firewall port and the default SSH port, which is port 22. SSH uses
the TCP protocol.
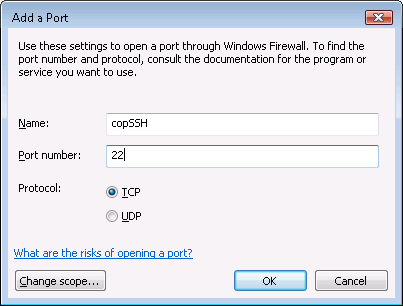
I clicked on Ok and then OK again to create the firewall rule for copSSH. I was then able to use PuTTY to log into the system from another system.
If you would like to use another port other than the default port of 22,
you need to edit the sshd_config file, which you will find within
the etc directory beneath the directory in which you installed
copSSH, e.g. \Program Files\copSSH\etc\sshd_config.
I suggest editing the file with WordPad rather than Notepad, because WordPad can handle the end of line characters used in the file so that each line appears one beneath the other rather than all lines appearing as one long line as they will in Notepad. WordPad can deal with the end of line character used on Unix and Linux systems better than Notepad. The file uses the linefeed character common for files on Unix and Linux systems rather than the combination of carriage return and linefeed characters that Microsoft Windows uses.
To change the port, locate the line below. Remove the "#" from the beginning of the line, which turns the line into a comment line. Then replace 22 with whatever number you wish to use for the port.
#Port 22
When you've changed the port, you will need to restart the SSH server service,
which you can do by rebooting or simply stopping and restarting the service.
To stop and restart the service from the command line, obtain a command prompt.
If you aren't logged into an administrator account, you can use the command
runas /user:administrator cmd from a command prompt to open
another command prompt window under the administrator account.
C:\>net stop "Openssh SSHD" The Openssh SSHD service is stopping. The Openssh SSHD service was stopped successfully. C:\>net start "Openssh SSHD" The Openssh SSHD service is starting. The Openssh SSHD service was started successfully.
You can verify copSSH is listening on the new port using the
netstat command. E.g., if you set the port to 5622, you
could use the command below:
C:\>netstat -an | find "5622" TCP 0.0.0.0:5622 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING

