Thu, Apr 30, 2015 11:17 pm
Forgetting a certificate in Firefox
While using a MacBook Pro with Firefox ESR 31.6.0, I needed to have it
"forget" a certificate for a website that I had it temporarily accept,
because of an issue with the site's certificate. The process for doing so
is as follows:
-
In Firefox, click on the icon of three short horizontal bars at the
upper, right-hand corner of the Firefox window, which will give you a menu
where you should select Preferences.
-
Select Advanced and click on the Certificates tab under
it.
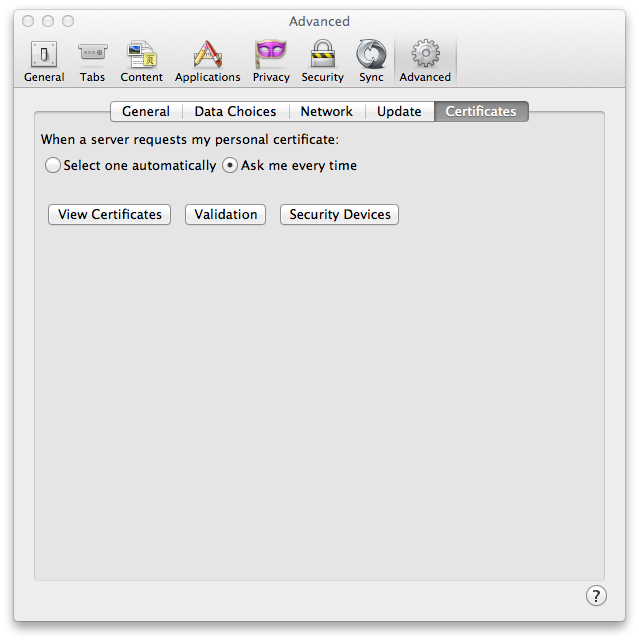
-
Click on View Certificates.
-
Click on the Servers tab.
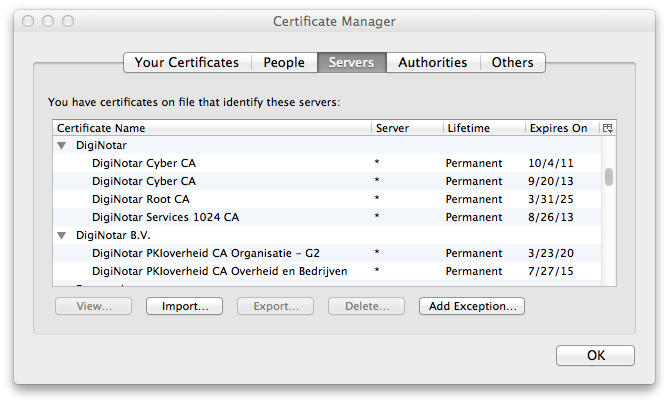
-
Locate the server for which you wish to delete the certificate. It will
have a lifetime value of "Permanent", if you permanently accepted it or
a value of "Temporary", if you only temporarily accepted it. Click on it
to highlight it, then click on the Delete button.
-
You will then see a message asking "Are you sure you want to delete these
server exceptions", which will show the server(s) you have selected and
also note "If you delete a server exception, you restore the usual security
checks for that server and require it uses a valid certficate." Click on
OK. If you want to view the certificate before deleting it, you
can click on the View button.
-
Click on OK to close the Certificate Manager window. You can
then close the Advanced window.
[/network/web/browser/firefox]
permanent link
Wed, Apr 29, 2015 11:17 pm
Importing text data from a webpage into Excel 2013
I needed to import a whitelist consisting of a list of
fully
qualified domain names from a web page into a Microsoft Excel
spreadsheet. The web page was just a text file with one entry per line,
which made it easy to import data directly from the page in Excel 2013.
The steps to import such data from a web page are as follows:
- Click on Data from the menu at the
top of the Excel window.
- Select Get External Data and From
Web.
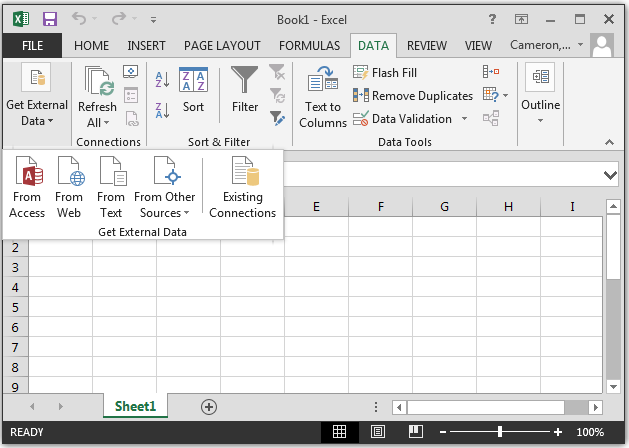
-
Type the URL for the webpage from which you wish to obtain the data
into the Address bar of the New Web Query window which will
have opened.
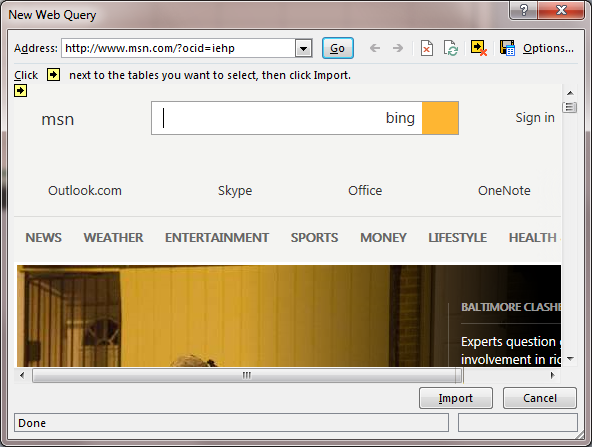
-
The contents of the webpage will be displayed and you can click on
the Import button.
-
You will then be asked "Where do you want to put the data?" The default
location will be $A$1, i.e., the cell in the first column and first row.
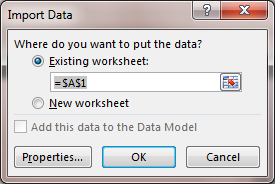
You can change the location or leave it as is and then click on
OK to have the data inserted in the sheet in the Excel workbook
If you need to update the data from the webpage when working in the
spreadsheet later, you can select Refresh All all from the Excel
toolbar and then select Refresh.
The contents of the sheet will then be refreshed with the latest data
from the web page.
[/os/windows/office/excel]
permanent link
Tue, Apr 28, 2015 10:51 pm
Checking wifi signal strength from the command line on OS X
I took a friend to a VA hospital today. I took my MacBook Pro laptop
with me and while I was there I used the wireless guest service at
the facility. The performance of the wireless service was awful
today as it was on a previous visit. To determine if the problem
might be attributable to signal strength, I used the
airport
command, which is available on OS X systems. The utility is located in
/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/.
Help information on the command is available using
airport -h.
$ /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport -h
Supported arguments:
-c[<arg>] --channel=[<arg>] Set arbitrary channel on the card
-z --disassociate Disassociate from any network
-I --getinfo Print current wireless status, e.g. signal info, BSSID, port type etc.
-s[<arg>] --scan=[<arg>] Perform a wireless broadcast scan.
Will perform a directed scan if the optional <arg> is provided
-x --xml Print info as XML
-P --psk Create PSK from specified pass phrase and SSID.
The following additional arguments must be specified with this command:
--password=<arg> Specify a WPA password
--ssid=<arg> Specify SSID when creating a PSK
-h --help Show this helpTo view the status for a wireless connection, use airport -I
or airport --getinfo.
$ /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport -I
agrCtlRSSI: -67
agrExtRSSI: 0
agrCtlNoise: -86
agrExtNoise: 0
state: running
op mode: station
lastTxRate: 7
maxRate: 144
lastAssocStatus: 0
802.11 auth: open
link auth: none
BSSID: ec:44:76:81:e4:40
SSID: VA Internet
MCS: 0
channel: 11The signal strength for a connection is the value for
agrCtlRSSI. "RSSI" stands for
received signal strength
indication. The higher the number, the stronger the wireless signal.
The maximum value that may be reported will depend on the wireless
devices being used. Cisco Systems wireless cards have a maximum value of
100 while Wi-Fi chipsets from Atheros will return a value from 0 to 128.
For Apple OS X systems, the value will range from a high of 0 down to
minus 100 (-100). The closer the number is to zero, the stronger the signal
while the closer the number is to negative 100, the weaker the signal
strength.
Since I only wanted to check the signal strength initially, I looked just
for that value. The signal strength seemed to be ok for the waiting room
I was in, though not terrific.
$ /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport -I | grep agrCtlRSSI
agrCtlRSSI: -74
$ /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport -I | grep agrCtlRSSI
agrCtlRSSI: -68[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x/wireless]
permanent link
Mon, Apr 27, 2015 11:30 pm
Mailman moderation bit
If you go to the membership management page for a
Mailman
mailing list, you will see a checkbox next to every member's address
in a "mod" column and an option to "Set everyone's moderation bit,
including those members not currently visible" near the bottom of
the web page. If you check the mod checkbox next to the member's
address, the list member will not be able to send messages to the
list without the message being approved by the list owner or a
moderator for the list.
When the box is checked for a member, postings from the member are
held and administrators are notified of their existence. They may
then approve or reject postings via the web interface. If unchecked
postings to the list are immediately delivered to list membership.
If a list is to be used only for announcements from the list owner
and designated moderators, then everyone else should have the box checked.
Note: Applies to Mailman 2.1.14 as well as other versions.
References:
-
GNU Mailman List Management Guide v 2.0
GNU Mailman Documentation
[/network/email/mailing_list/mailman]
permanent link
Sun, Apr 26, 2015 9:47 pm
Changing the colors for a Terminal tab on OS X
The Terminal application in
Applications/Utilities allows one
to obtain a shell prompt on a Mac OS X system. You can specify the color
scheme to use when opening a new tab. The default color scheme is "Basic",
i.e., black text on a white background, but you can also choose from
the following:
Grass
Homebrew
Man Page
Novel
Ocean
Pro
Red Sands
Silver Aerogel
Solid Colors
If after making a selection while working in that tab, you
wish to change the colors, you can do so. E.g., if I had selected
the "grass" color scheme, but wanted to change from yellow text on
a green background to black text on a white background, I could so
so by taking the following steps while working in that Terminal tab.
-
From the Terminal menu, select Show Inspector or hit
Command-I to bring up the Inspector window.
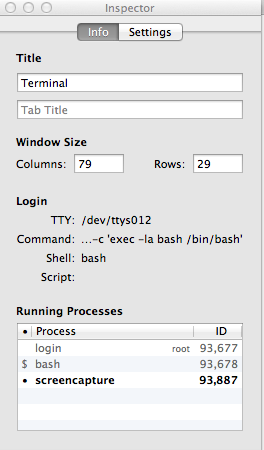
-
Click on Settings. You will see the current color scheme
highlighted, e.g., "Grass" in this instance.
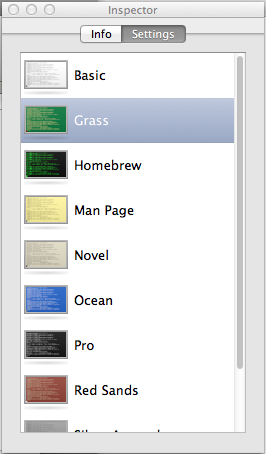
-
Click on the new color scheme you wish to use, e.g., "Basic" for black text
on a white background. As soon as you click on a new color scheme, the
foreground and background colors will change.
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Sat, Apr 25, 2015 10:41 pm
Using netcat to simulate a web server
If you have a Mac OS X system or a Linux system, you can listen for
connections from web browsers on the system by utilizing the
netcat utility,
which you can run by issuing the
nc command from a Terminal
window, i.e., a shell prompt. The Terminal application is found in
Applications/Utilities on a Mac OS X system.
You won't get the functionality provided by installing web server
software, such as the
Apache HTTP
Server, but you can use the command for testing or to provide
one page that is visible to thers from their browsers. As an example,
the command below instructs netcat to listen on port 8080 for
connections and display the file index.html when the system is
accessed on that port. If you pick a port above 1024, such as 8080
rather than 80, you don't need root (admin) privileges in order to
have the system listen on the port, but, if you don't use the default port
of 80, you need to specify the port used in the URL, e.g.,
http://www.example.com:80, when you try to connect with a browser.
nc -kl 8080 < index.html
In the above example, two options for netcat, -l
and -k are combined into -kl. Their meaning
and other options can be displayed by issuing the command nc -h.
-k Forces nc to stay listening for another connection after its cur-
rent connection is completed. It is an error to use this option
without the -l option.
-l Used to specify that nc should listen for an incoming connection
rather than initiate a connection to a remote host. It is an
error to use this option in conjunction with the -p, -s, or -z
options. Additionally, any timeouts specified with the -w option
are ignored.If you are running the command on an OS X system, you may see a
window appear asking whether you wish to allow netcat to receive
incoming connections.
To access the web page from a browser on the system on which you run the
command, or from another system, you will need to specify an appropriate IP
address for the system, which you can get
using the ifconfig -a command, or a fully
qualified domain name for it. If the system is accessible from
the Internet, you can determine what IP address others need to use by
visiting WhatIsMyIP.
E.g., suppose the IP address for the system is 192.168.1.5. That IP
address is
private IP address space, so wouldn't be accessible from the Internet, but
you would substitute whatever IP address others would see for the system, if
you had a system that was accessible from the Internet, e.g., whatever address
WhatIsMyIP would show if you visited
that website using a browser on the system. If you put in
http://192.168.1.5:8080, or substituting whatever port number
you picked instead of 8080, in a web browser, then you should
see the contents of index.html displayed.
If you only need access from a browser on the system itself, then you
can just put in the system's
localhost, aka, local loopback, address, which is 127.0.0.1. E.g., if you
had netcat listen for connections on ort 8080, you could use
http://127.0.0.1:8080.
You can use whatever file name you like, e.g., test123.html will work equally
as well. If you specified that file name, using http://192.168.1.5:8080
would display the contents of that file without it being specified
in the address bar of the browser.
Some browsers may expect the normal status returned by a web server when
a page is accessed, so you may want to include the following line at the top
of index.html or whatever file you specify. Follow the line with a blank line.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
E.g., below is a sample index.html file that could be used.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Testing</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1 align="Center">Test</H1>
<a href="http://support.moonpoint.com">Moonpoint Support</a><br>
</BODY>
</HTML>
If you don't include the "HTTP/1.1 200 OK" line followed by a blank line,
you may see a message such as "The connection was reset" or some other error
message, so I would recommend including it.
Until you hit Control-C at the command prompt window, netcat
will continue to listen for connections and you will see the HTTP commands
issued by browsers. E.g., I might see the following when
http://192.168.1.5:8080 is placed in the address bar of
Firefox.
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.1.5:8080
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.8; rv:31.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/31.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.1.5:8080
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.8; rv:31.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/31.0
Accept: image/png,image/*;q=0.8,*/*;q=0.5
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
Note: if the system on which you are running the netcat command is running
host-based firewall software, you may need to configure that software to
allow incoming connections on the port you specified in the netcat command
in order for connectivity to work. E.g., see
Opening a firewall port for Firewalld from the command line for
the command to use on a CentOS Linux system running FirewallD.
References:
-
One command line web server on port 80 using nc (netcat)
Date: August 31, 2011
commandlinefu.com
[/network/tools/netcat]
permanent link
Fri, Apr 24, 2015 5:07 pm
Opening a firewall port for Firewalld from the command line
You can see what services and ports already have firewall rules permitting
access to the ports on a CentOS system using
FirewallD for the
firewall service from a shell prompt with
firewall-cmd
--list-services and
firewall-cmd --list-ports.
# firewall-cmd --list-services
dhcpv6-client http pop3s smtp ssh
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
110/tcp 4343/tcp 143/tcp
If you wish to permit access on an additional port you can use
the --add-port option. Specify the zone to which
the rule should apply with --zone and specify UDP or TCP
with /protocol after the port number, where
protocol is either udp or tcp.
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
110/tcp 4343/tcp 8080/tcp 143/tcp
Note: in the above example the firewall rule is only added temporarily; it
won't persist after a reboot of the system. To make the rule permanent requires
the use of the --permanent option and a restart of the
firewall service with systemctl restart firewalld.service or
firewall-cmd --reload. E.g.:
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
systemctl restart firewalld.service
If you wish to see a list of the configured zones on the system, use
the --get-zones option.
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zones
block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work
If you wish to see the open ports for a particular zone, you can specify
the zone with --zone=. E.g.:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
110/tcp 4343/tcp 8080/tcp 143/tcp
If you wish to remove access to a port for which you have permitted
connectivity, you can use the --remove-port option. If you
specify a port for which there is no rule permitting access, you will
see a "Warning: NOT_ENABLED" message. E.g.:
# firewall-cmd --remove-port=443/tcp
Warning: NOT_ENABLED
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
110/tcp 4343/tcp 8080/tcp 143/tcp
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --remove-port=8080/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
110/tcp 4343/tcp 143/tcp
If you are removing a permanent entry, specify the --permanent
option and reload the firewall softward afterwards. E.g.:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --remove-port=8080/tcp --permanent
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
References:
-
Monitoring Failed SSH Logins to a CentOS System
Date: November 9, 2014
MoonPoint Support
-
RHEL7: How to get started with Firewalld.
Last updated on April 14, 2015
CertDepot
[/os/unix/linux/centos]
permanent link
Thu, Apr 23, 2015 9:30 pm
Enabling audio on a Windows Server 2012 system
By default, Windows Server 2012 doesn't have the audio service enabled, likely
because it won't be needed on many servers, which may not even have
speakers attached to them. You can enable the service by several different
methods. You can run
services.msc and start the
Windows Audio
service. You can also change the startup type from manual to
automatic to have the service start automatically when the system boots.
Another method for enabling the audio service is to right-click on the
speaker icon in the notification area at the lower, right-hand corner of
the screen and choose
Playback devices. You will then see a message
asking whether you wish to enable the audio service. If you choose "Yes",
the service will be enabled and the startup type will be changed to automatic
so the service will start whenever Windows loads.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/server2012]
permanent link
Wed, Apr 22, 2015 9:47 pm
Opening the Device Manager from a command prompt on Windows 8
To open the
Device Manager window on Windows 8 from a command prompt,
take the following steps:
-
Right-click on the Start button in the lower-left corner of the
screen.
-
If you are logged in under a standard user account and only want to
view device settings, you can choose Command Prompt. If you may
need to change settings and aren't logged in under an account in the
administrators group, choose Command Prompt (Admin). If you
choose the latter, you will be prompted for administrator credentials;
provide a user name and password for an administrator account. When
you choose Command Prompt (Admin), the title of the window
that opens is "Administrator Command Prompt" versus "Command Prompt"
if you open the command prompt window using a standard account.
-
When the Command Prompt window opens type
devmgmt.msc at the
command line and hit Enter. If you are logged on with an account
that does not have administrator privileges and haven't opened an
Administrator Command Prompt window, you will see the message below:
You are logged on as a standard user. You can view device settings in Device
Manager, but you must be logged on as an administrator to make changes.
You can then click on the OK button to view information
for devices listed in the Device Manager. If you've run
devmgmt.msc from an Administrator Command Prompt window you
will have view and modification capabilities.
[/os/windows/win8]
permanent link
Tue, Apr 21, 2015 11:25 pm
Checking the battery temperature for a MacBook Pro laptop
I wanted to check the temperature of components in a MacBook Pro
laptop running OS X 10.8.5, aka
Mountain Lion,
from the command line. A
Bash script by
jondthompson, which
is a
fork of a script posted by
earlonrails, to check the
battery temperature that can be run from a Terminal window can be found at
GitHub Gist at
battery_temperature.sh. I've also included the code below.
#!/bin/bash
# battery_temperature for mac osx 10.9.2
if [ `uname` == "Darwin" ]; then
if [ "$1" == "-h" ]; then
echo "Usage: $(basename $0 ".sh") [option]"
echo " -l also show Model Name and Processor Name"
echo " -h display this help message"
exit
fi
# -l display Model Name and Processor Name
if [ "$1" == "-l" ]; then
system_profiler SPHardwareDataType | awk '/Model Name/ || /Processor Name/' | sed 's/[^:]*: //' | awk '{ printf $0 " " }'
echo
fi
# sensor data
temperature=`ioreg -r -n AppleSmartBattery | grep Temperature | cut -c23-`
temperature_celsius=`echo "scale = 2; $temperature / 100.0" | bc`
echo "AppleSmartBattery Temperature: "
echo $temperature_celsius °C
temperature_fahrenheit=`echo "scale = 2; ($temperature_celsius * (9 / 5)) + 32.0" | bc`
echo $temperature_fahrenheit °F
# error message if unsupported machine
else
echo -e "\nThis appears not to be an OS X machine\n"
fi
After making the script executable, when I ran it on a 15-inch, Mid 2009
MacBook Pro laptop, I saw the following:
$ chmod +x battery_temperature.sh
$ ./battery_temperature.sh
AppleSmartBattery Temperature:
30.46 °C
86.82 °F
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Mon, Apr 20, 2015 10:53 pm
Disabling Automatic Restart for Windows Server 2012 Essentials
As with other verions of Microsoft Windows, such as Windows XP, Vista, 7,
8, you may find Microsoft
Windows Server 2012
and the Windows Server 2012 Essentials edition rebooting the system at
inopportune times for updates. You can temporarily delay the shutdown by
issuing the command
net stop "windows update" at a command
prompt. Note: you need to open an admin command prompt to do so, which
you can do by moving the mouse pointer to the lower, left-hand corner
of the screen, then right-clicking on the
Start button when it
appears and choosing
Command Prompt (Admin). But that wil only
postpone the reboot, because Windows will later restart the service on
its own, even if you don't reboot. You can determine if it has restarted
by reissuing the command. You will see a message "The Windows Update
service is not started", if it isn't running.
You can pemanently disable the automatic restart by changing the
group policy for
the system by running gpedit.msc, which you can run by
issuing the command gpedit at a command prompt or by
right-clicking on the Start button, choosing Run and
then typing gpedit.msc and hitting Enter. When
the Local Group Policy Editor window opens, navigate to
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates >
Windows Components > Windows Update.
In the right pane of the window, you will see "No auto-restart with logged on
users for scheduled automatic updates installations". Change the setting
from "Not Configured" to "Enabled".
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/server2012]
permanent link
Thu, Apr 16, 2015 11:16 pm
Adding a Konica Minolta BizHub 363 printer from the command line on OS X
I needed to add a Konica Minolta BizHub 363 multifunction device as a
printer on my MacBook Pro laptop, since the default printer was
inaccessible today. So I checked if there was a printer driver for it
already on the laptop in
/Library/Printers/PPDs/Contents/Resources. I saw one there,
so added it from a Terminal window, i.e., a shell prompt.
$ ls -l /Library/Printers/PPDs/Contents/Resources | grep -i Konica | grep 363
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 42781 Sep 3 2012 KONICAMINOLTA363.gz
$ lpadmin -p "192.168.233.8" -v "lpd://192.168.233.8" -D "Konica Minolta BizHub 363 MFD" -L "Building 14 Room E171" -P "/Library/Printers/PPDs/Contents/Resources/KONICAMINOLTA363.gz" -E
When adding a printer from the command line on an OS X system, you
can specify the IP address of the printer with the -p
(lowercase "p") argument to the lpadmin command. Other
arguments for the command include the following:
-v "device-uri"
Sets the device-uri attribute of the printer queue. Use the -v
option with the lpinfo(8) command to get a list of supported
device URIs and schemes.
-D "info"
Provides a textual description of the destination.
-L "location"
Provides a textual location of the destination.
-P ppd-file
Specifies a PostScript Printer Description file to use with the
printer. If specified, this option overrides the -i option
(interface script).The text enclosed in quotes after the -D can be any
description you want to give to the printer and the -L is
any text you wish to use to indicate the location of the printer.
For the -P (uppercase "P") option, I referenced the
Konica Minolta BizHub 363
PostScript Printer Description file I saw on the system.
The -v option is followed by a
uniform
resource identifier (URI). In this case that was lpd://
followed by the IP address of the printer because the printer supports the
Line
Printer Daemon protocol.
After you've added a printer, you can verify that it has been added
using the lpstat command. E.g., lptstat -p -d
shows all of the printers added to the system and the default printer for
the system.
-d
Shows the current default destination.
-h server[:port]
Specifies an alternate server.
-l
Shows a long listing of printers, classes, or jobs.
-o [destination(s)]
Shows the jobs queue on the specified destinations. If no destina-
tions are specified all jobs are shown.
-p [printer(s)]
Shows the printers and whether or not they are enabled for print-
ing. If no printers are specified then all printers are listed.E.g., I can see that the printer I added is enabled. I can also see
that the default printer is at 192.168.234.59, which was inaccessible to
me today because the room it is in was locked.
$ lpstat -p -d
printer 192.168.233.8 is idle. enabled since Thu Apr 16 14:12:21 2015
printer 192.168.234.59 is idle. enabled since Thu Apr 16 13:59:17 2015
Data file sent successfully.
printer _192_168_232_14 disabled since Wed Aug 17 14:52:55 2011 -
/usr/libexec/cups/backend/lpd failed
printer _192_168_235_214 disabled since Tue Dec 27 09:55:45 2011 -
Printer not responding!
printer _192_168_75_20 is idle. enabled since Sat Jun 29 10:21:21 2013
system default destination: 192.168.234.59
References:
-
Adding a printer from the command line on an OS X system
Date: August 7, 2014
MoonPoint Support
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Tue, Apr 14, 2015 10:22 pm
Locating EIN in QuickBooks 2011
To locate the U.S. Federal Employer Identification Number (EIN) issued by
the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in QuickBooks 2011, open the company
file using a QuickBooks admin account then take the following steps:
- Select Company from the menu bar.
- Select Company Information. The EIN is
in the Company Identification section.
The information can only be viewed or modified from a QuickBooks admin
account.
[/financial]
permanent link
Mon, Apr 13, 2015 11:25 pm
Finding files and/or directories with no owners
On a Unix/Linux system, you can locate files or directories that don't belong
to a valid user account or group on the system with the command
find and the
-nouser or
-nogroup option.
-nogroup
No group corresponds to file's numeric group ID.
-nouser
No user corresponds to file's numeric user ID.
E.g., to find any such files in the current directory and below it, I can use
find . -nouser
# find . -nouser
./temp
./temp/bounced.txt
./temp/._Oct14(10-2).pdf
./temp/._Oct14.doc
The above example shows that the directory temp and three
files within it don't have a valid owner. Checking them with the ls
command, I see a long sequence of digits listed for the ower and
group instead of an account listed in /etc/passwd or
/etc/group.
# ls -ld temp
drwxr-xr-x. 2 723184451 1286109195 74 Feb 13 17:09 temp
# ls -al temp
total 60
drwxr-xr-x. 2 723184451 1286109195 74 Feb 13 17:09 .
drwx------. 8 jasmith1 jasmith1 4096 Apr 10 22:26 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 723184451 1286109195 45333 Oct 6 2014 bounced.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 723184451 1286109195 192 Oct 6 2014 ._Oct14(10-2).pdf
-rw-r--r--. 1 723184451 1286109195 192 Oct 6 2014 ._Oct14.doc
Files or directories with no group listed in /etc/group
corresponding to the numeric group id for the file or directory
can be found with find . -nogroup to search in and beneath
the current directory or find / -nogroup to search starting
at the root directory.
# find . -nogroup
./temp
./temp/bounced.txt
./temp/._Oct14(10-2).pdf
./temp/._Oct14.doc
./mail
./mail/.imap
./mail/.imap/INBOX
./mail/.imap/INBOX/dovecot.index.cache
./mail/.imap/INBOX/dovecot.index
./mail/.imap/INBOX/dovecot.index.log
# ls -ld mail
drwx------. 3 jasmith1 508 18 Sep 29 2014 mail
# ls -al mail/.imap/INBOX
total 20
drwx------. 2 jasmith1 508 76 Sep 29 2014 .
drwx------. 3 jasmith1 508 18 Sep 29 2014 ..
-rw-------. 1 jasmith1 508 144 Sep 29 2014 dovecot.index
-rw-------. 1 jasmith1 508 10272 Sep 29 2014 dovecot.index.cache
-rw-------. 1 jasmith1 508 96 Sep 29 2014 dovecot.index.log
You can use the -o option for "or" to find files and
directories that either don't have a user account associated with the numeric
user id or don't have a group associated with the numeric group id. E.g.,
find . -nogroup -o -nouser.
If you delete an account or group from the system, files or directories
that remain that had that owner or group will then be displayed with the
user id and group id associated with the account or group that was deleted
when you use the ls command.
[/os/unix/commands]
permanent link
Sun, Apr 12, 2015 3:46 pm
Using offset in Apache OpenOffice Calc
As does Microsoft Excel,
Apache OpenOffice calc provides an
offset function that allows
you to calculate a value based on the contents of a cell that is a specified
distance in rows and columns from a particular cell. The syntax for calc is
as follows:
OFFSET
Returns the value of a cell offset by a certain number of rows and
columns from a given reference point.
Syntax
OFFSET(Reference; Rows; Columns; Height; Width)
Reference is the reference from which the function searches for
the new reference.
Rows is the number of rows by which the reference was corrected
up (negative value) or down.
Columns (optional) is the number of columns by which the
reference was corrected to the left (negative value) or to the right.
Height (optional) is the vertical height for an area that
starts at the new reference position.
Width (optional) is the horizontal width for an area that starts at the new reference position.
Arguments Rows and Columns must not lead to zero or negative
start row or column.
Arguments Height and Width must not lead to zero or negative
count of rows or columns.
In the OpenOffice Calc functions, parameters marked as "optional" can be
left out only when no parameter follows. For example, in a function with
four parameters, where the last two parameters are marked as "optional",
you can leave out parameter 4 or parameters 3 and 4, but you cannot
leave out parameter 3 alone.
Example
=OFFSET(A1;2;2) returns the value in cell C3 (A1 moved by two rows and two columns down). If C3 contains the value 100 this function returns the value 100.
=OFFSET(B2:C3;1;1) returns a reference to B2:C3 moved down by 1 row and
one column to the right (C3:D4).
=OFFSET(B2:C3;-1;-1) returns a reference to B2:C3 moved up by 1 row and
one column to the left (A1:B2).
=OFFSET(B2:C3;0;0;3;4) returns a reference to B2:C3 resized to 3 rows
and 4 columns (B2:E4).
=OFFSET(B2:C3;1;0;3;4) returns a reference to B2:C3 moved down by one
row resized to 3 rows and 4 columns (B2:E4).
=SUM(OFFSET(A1;2;2;5;6)) determines the total of the area that starts in
cell C3 and has a height of 5 rows and a width of 6 columns (area=C3:H7).
[ More Info ]
[/software/openoffice]
permanent link
Fri, Apr 10, 2015 10:37 pm
Sending messages and files with mailx
On a Linux/Unix system or OS X system, a very quick way to send email
messages and files by email from a shell prompt, aka command line,
is to use the
mailx utility.
If you wish to send the contents of a file as the body of a message, you
can use a command like the following one:
$ mailx someone@example.com <report.txt
The above command would send the contents of the file report.txt
to someone@example.com. The contents would be inserted within the body of
the message. In the above case, the message would have no subject. You can
use the -s option to the command to provide a subject for the
message. E.g.:
$ mailx -s "Just a test" someone@example.com <report.txt
The above command would send the same message as the previous one, but
this time with a subject line of "Just a test". If the subject line contains
a space, you must enclose the subject within quotes.
If, instead of sending a file's contents in the body of the message, you
wish to send it as an attchment, you can use the -a option on
Linux/Unix systems, but not on OS X, since the -a option isn't
supported for mailx for that operating system.
$ mailx -s "another test" -a report.txt -b someoneelse@example2.com,jdoe@anothersite.com someone@example.com
A test message with an attachment.
Also sending to two BCC email addresses
EOT
In the above example, the file report.txt is sent as an
attachment to the message with someone@example.com used as the "to" address.
I also sent the message to two additional addresses
as blind carbon copy (BCC) addreses using the -b option. When
using the -b option to send to multiple email addresses,
separate the addresses with a comma. Instead of putting the contents of the
file report.txt in the body, the body in the above example
consists of the two lines starting with "A test message". You can provide
the body of the message by simply typing the mailx command line then hitting
return and then starting typing whatever you want to appear in the body of
the message. When you are finished, hit Ctrl-D, i.e., the
Ctrl and D keys simultaneously. You will then see
EOT appear for the end of text and the message will be transmitted.
If you wish to put email addresses in the carbon copy (CC) field, use
-c, instead of -b. As with the -b option,
separate multiple email addresses with a comma.
If you wish to see if the message has been transmitted from the sending
system, you can use the mailq command. If it hasn't been
transmitted you will see the message still in the queue as in the example
below from a Mac OS X system.
$ mailq
-Queue ID- --Size-- ----Arrival Time---- -Sender/Recipient-------
AEADBD2536AA* 370 Fri Apr 10 22:10:44 jsmith@GSOD000962737L.local
someone@example.com
someoneelse@example2.comOn a Linux/Unix system, you will need to run the mailq command as
root or you can run the command with sudo, if the account you are using
is in the sudoers file.
Though, if the message isn't shown in the queue, there still could
have been a failed delivery attempt. E.g., a short time after issuing
the mailq command above on a OS X system, when I reissued the command I
saw the following indicating the system could not send the email via
mailx.
$ mailq
postqueue: fatal: Queue report unavailable - mail system is down
[/network/email/mailx]
permanent link
Thu, Apr 09, 2015 11:11 pm
Check for available updates from the command line under OS X
If you wish to know what updates are available for a Mac OS X system,
you can use the system software update tool, softwareupdate, to do so by
issuing the command
sudo softwareupdate -l, if the
account you are logged in under has administrative privileges; if so, enter
the password for that account when prompted. A command line prompt is
available on OS X by running the terminal application found in the
Applications/Utilities folder.
$ sudo softwareupdate -l
Password:
Software Update Tool
Copyright 2002-2010 Apple
2015-04-09 22:51:06.156 softwareupdate[30930:3903] No alternate URLs found for packageId MobileDevice
Software Update found the following new or updated software:
* RemoteDesktopClient-3.8.2 v1.1
Remote Desktop Client Update (3.8.2 v1.1), 7123K [recommended]
* SecUpd2015-004MtLion-1.0
Security Update 2015-004 (1.0), 179583K [recommended] [restart]
* Safari6.2.5MountainLion-6.2.5
Safari (6.2.5), 59025K [recommended]
* AirPortUtility-6.3.1
AirPort Utility (6.3.1), 21104K [recommended]
* iTunesXPatch-12.1.2
iTunes (12.1.2), 101172K [recommended]
* Mac App Store Update-1.0
Mac App Store Update (1.0), 3697K [recommended] [restart]
In the example output above, you can see that installing some of the
updates will require a restart afterwards to have the updates take effect.
If you don't precede the command with sudo, you will see a
message informing you that the command must be run as root.
$ softwareupdate
softwareupdate: Must be run as root
For a list of available options for the command, you can use
sudo softwareupdate -h.
$ sudo softwareupdate -h
Password:
usage: softwareupdate <mode> [<args> ...]
-l | --list List all appropriate updates
-d | --download Download Only
-i | --install Install
<label> ... specific updates
-a | --all all appropriate updates
-r | --recommended only recommended updates
--ignore <label> ... Ignore specific updates
--reset-ignored Clear all ignored updates
--schedule (on | off) Set automatic checking
-v | --verbose Enable verbose output
-h | --help Print this help
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Wed, Apr 08, 2015 8:46 pm
Hibernating a Windows 7 computer
You may be able to hibernate a Microsoft Windows 7 computer even if you
don't see the hibernate option listed when you hit
Ctrl-Alt-Del
and click on the power button but see only the
Shut down and
Sleep options or if you click on the Windows
Start
button and then click on the arrow head next to the shut down button and
see only the
Sleep option. Try getting a command prompt, instead,
which you can obtain by clicking on the
Start button and typing
cmd and hitting enter and then type
shutdown /h
or
shutdown /h /f if you also want running applications to be
forced to close. Not all PCs may support hibernate mode. You can issue the
command
powercfg -availablesleepstates at a command prompt to
see if hibernation mode is available on the system.
C:\>powercfg -availablesleepstates
The following sleep states are available on this system: Standby ( S3 ) Hibernat
e Hybrid Sleep
The following sleep states are not available on this system:
Standby (S1)
The system firmware does not support this standby state.
Standby (S2)
The system firmware does not support this standby state.Another option for the powercfg command, - hibernate
or -h, enables or disables hibernation. You can see
all available options with powercfg /?.
-HIBERNATE, -H
Enables-Disables the hibernate feature. Hibernate timeout is not
supported on all systems.
Usage: POWERCFG -H <ON|OFF>
POWERCFG -H -Size <PercentSize>
-Size Specifies the desired hiberfile size in percentage of the
total memory. The default size cannot be smaller than 50.
This switch will also enable the hiberfile automatically.
-AVAILABLESLEEPSTATES, -A
Reports the sleep states available on the system
Attempts to report reasons why sleep states are unavailable.
[/os/windows/win7]
permanent link
Mon, Apr 06, 2015 10:04 pm
Determining the version of the OS and applications under OS X
You can determine the version of applications installed on an OS X system
by clicking on the Apple icon in the upper, left-hand corner of the screen
then selecting
About This Mac, then
More Info, then
System Report, then
Software, and then clicking on
Applications beneath
Software. You will see a display
similar to the following one:
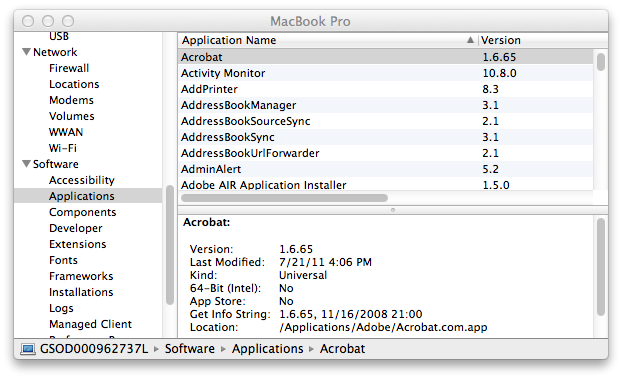
If you wish to determine the version number of an app from the command line,
if the application supports command line options, you may be able to use
one such as -v or -version to determine the version.
Or you can use the system_profiler SPApplicationsDataType
command to obtain a similar comprehensive list.
E.g., here are a few commands to determine the operating system
version and the version of a few common applications under OS X
from a command prompt, which can be obtained using the Terminal
application.
Determine the OS version with sw_vers.
$ sw_vers
ProductName: Mac OS X
ProductVersion: 10.8.5
BuildVersion: 12F45
The Wikipedia OS X
article provides the names given by Apple to each version. E.g., OS X
10.8.5 is called "Mountain Lion".
Determine the version of Java with java -version
$ java -version
java version "1.6.0_65"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.6.0_65-b14-462-11M4609)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 20.65-b04-462, mixed mode)
Determine the version of Firefox with
/Applications/Firefox.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox -v or
-version.
$ /Applications/Firefox.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox -v
Mozilla Firefox 31.5.0
$ /Applications/Firefox.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox -version
Mozilla Firefox 31.5.0
Determine the version of
GNU Image Manipulation Program
(GIMP) with
/Applications/Gimp.app/Contents/MacOS/gimp --version or
/Applications/Gimp.app/Contents/MacOS/gimp -v with the
-v option providing more details.
$ /Applications/Gimp.app/Contents/MacOS/gimp --version
Setting up environment...
Enabling internal python...
Locale black magic...
Launching GIMP...
GNU Image Manipulation Program version 2.8.10
$ /Applications/Gimp.app/Contents/MacOS/gimp -v
Setting up environment...
Enabling internal python...
Locale black magic...
Launching GIMP...
GNU Image Manipulation Program version 2.8.10
git-describe: GIMP_2_8_8-55-g9bb7eb0
using GEGL version 0.2.1 (compiled against version 0.2.1)
using GLib version 2.38.2 (compiled against version 2.38.2)
using GdkPixbuf version 2.30.1 (compiled against version 2.30.1)
using GTK+ version 2.24.22 (compiled against version 2.24.22)
using Pango version 1.36.0 (compiled against version 1.36.0)
using Fontconfig version 2.11.0 (compiled against version 2.11.0)
using Cairo version 1.12.16 (compiled against version 1.12.16)
If you would like to see all of the available command line options for
GIMP, you can use /Applications/Gimp.app/Contents/MacOS/gimp -?,
or -h, or --help, instead of the -?.
You can get the version for many applications at once using the command
system_profiler SPApplicationsDataType.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Sat, Apr 04, 2015 11:20 pm
Testing email delivery with SMTP commands
Telnet can be used from
a command line interface, aka shell prompt, to manually send commands to
an
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server to test email deliveries.
An SMTP server typically listens on port 25 for incoming connections from
mail clients or other email servers. So you could enter
telnet
mail.example.com 25 to connect to that port on a server, e.g.,
mail.example.com in this example, from a command line.
Telnet is available on Linux systems, or can be installed if it is not,
and is also available on Mac OS X systems where you can run the application
by using the Terminal application to obtain a shell prompt. Telnet was
available by default with early versions of Microsoft Windows, but that is
no longer the case. The free and open source
PuTTY program is an
excellent telnet client for Windows, however. To use it to connect to port
25 on an email server, you simply select Telnet as the connection
type and put 25 in the port field.
Once you've connected to port 25 on a mail server, the first command to
enter is either helo or ehlo. Issuing that command
is akin to saying "hello" when you meet someone. The command is usually
followed by the name of the system from which you are connecting, e.g.,
helo me.example.com if you ran the telnet command on a system
with a
fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of me.example.com. But you can follow
the helo or ehlo command with anything, just as
you could say "hello, I'm Paul" when you met someone even if your name was
Peter.
Ehlo is a command that is part of
Extended SMTP (ESMTP),
aka "Enhanced SMTP", which defines protocol extensions for the SMTP
protocol. Ehlo is shorthand for "Extended Hello" and in the
protocol extensions of ESMTP provides a similar role of an introduction.
If the email server to which you are connecting supports the protocol
extensions of ESMTP, it will reply with a list of the keywords it supports
with each preceded by the code 250 as shown below:
$ telnet smtp.mandrillapp.com 25
Trying 54.158.189.65...
Connected to smtp.mandrillapp.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 smtp.mandrillapp.com ESMTP
ehlo moonpoint.com
250-ip-10-81-192-73
250-PIPELINING
250-SIZE 26214400
250-STARTTLS
250-AUTH PLAIN LOGIN
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250 8BITMIME
If the server doesn't support ESMTP, it will return error code 500, instead.
ESMTP client software can then try either HELO, instead, or
issue the QUIT command to terminate the connection to the server.
If the email server doesn't require authentication, you can then issue
commands specifying the "from" and "to" addresses for the email message as
shown below:
$ telnet mail.example.com 25
Trying 192.168.101.222...
Connected to mail.example.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 mail.example.com ESMTP Sendmail 8.14.7/8.14.7; Sat, 4 Apr 2015 22:02:39 -0400
mail from: testing@example.com
250 2.1.0 testing@example.com... Sender ok
rcpt to: moonpoint@example.com
250 2.1.5 moonpoint@example.com... Recipient ok
data
354 Enter mail, end with "." on a line by itself
This is a test.
.
250 2.0.0 t3520758032350 Message accepted for delivery
quit
221 2.0.0 mail.example.com closing connection
Connection closed by foreign host.
First you issue the command mail from: followed by the
email address that is the "from" address. You then issue the command
rcpt to: followed by the destination email address. The
content of the message is specified by typing data then hitting
Enter and then typing the contents of the email you wish to send.
To terminate the content, type a period by itself as the first character
on a line and then hit Enter. That's all you need to send an email
message and you can then terminate the connetion to the server with the
Quit command.
In the example above, the message you send won't have a subject, because
none was specified. You can specify the subject by entering Subject:
after the Data command. You can also include From:
and To: in the data that follows the data
command. Those don't even have to be the same as what you speficied with the
mail from: and rcpt to commands. If you enter
a From: and To: address after the data
command, those will be what the recipient sees when he or she views the
message. E.g., you could use rcpt to: mary@example.com to
send an email to mary@example.com, but put a bogus address after the
data command, such as From: bogusemail@nonexistent.com
and the email would still be delivered successfully to Mary's mary@example.com
email address, but when she viewed the message it would appear to her it was
sent to bogusemail@nonexistent.com.
$ telnet mail.example.com 25
Trying 192.168.101.222...
Connected to mail.example.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 mail.example.com ESMTP Sendmail 8.14.7/8.14.7; Sat, 4 Apr 2015 22:17:16 -0400
mail from: testing@example.com
250 2.1.0 testing@example.com... Sender ok
rcpt to: someone@example.com
250 2.1.5 someone@example.com... Recipient ok
rcpt to: someoneelse@somesite.com
250 2.1.5 someoneelse@somesite.com... Recipient ok
data
354 Enter mail, end with "." on a line by itself
From: someone@example.com
To: bogusemail@example.com
Subject: A Test
Just a test.
.
250 2.0.0 t352HGPe003192 Message accepted for delivery
QUIT
221 2.0.0 mail.example.com closing connection
Connection closed by foreign host.
$
In the example above, I skipped the introduction using helo
or ehlo and went straight to rcpt to. I then
entered rcpt to: someone@example.com. When I entered the
rcpt to: someoneelse@somesite.com command I wasn't adding a
second delivery destination for the email but replacing the prior email
recipient; you can just re-enter commands if you've made typos. I then
changed the "from" address that the recipient would see
with From: someone@example.com and also inserted
To: bogusemail@example.com. There's no validation of the
from address at any part of this process, which shows just
how easy it is to spoof the "from" address in an email message, which is
why you should never assume that the "from" address in an email message
reflects the actual sender. Spammers and malware distributors often insert
fake "from" addresses in their email. The email server will check that
the rcpt to: address is a valid email address on the server or
the sender is allowed to "relay" email based on the sender's IP address,
email address, or authentication, but the "to" address seen in a message
when viewed in an email client also doesn't necessarily reflect the one
used in the rcpt to address.
If the rcpt to address isn't a valid email account on the
server and if the server isn't configured to "relay" email to addresses that
exist on other servers, or at least not for the sender of a particular message,
it will respond with a "relaying denied" message.
s telnet example.com 25
Trying 192.168.101.222...
Connected to example.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 localhost.localdomain ESMTP Sendmail 8.14.7/8.14.7; Sat, 4 Apr 2015 22:15:24 -0400
ehlo example.com
250-example.com Hello me.somewhere.com [10.0.1.12], pleased to meet you
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-PIPELINING
250-8BITMIME
250-SIZE
250-DSN
250-ETRN
250-AUTH DIGEST-MD5 CRAM-MD5
250-DELIVERBY
250 HELP
mail from: testing@example.com
250 2.1.0 testing@example.com... Sender ok
rcpt to: someone@someothersite.com
550 5.7.1 someone@someothersite.com... Relaying denied
The above commands can be used by one email server communicating with
another, e.g., a sender's email server communicating with a recipient's email
server. They can also be used by a client email application, e.g.,
Thunderbird
or Microsoft Outlook. If you are sending email from an email client to an
email server, you may be required to authenticate with that server first
with a userid and password before the server will allow the client to
transmit email through it,though. This is a mechanism to block
spammers from sending email via the server. You can use the AUTH
PLAIN command to transmit those credentials if the email server
supports that command. E.g., in the example below the server supports
that command, since it returns the code 250 followed by "AUTH PLAIN"
after an ehlo command is issued, so I can authenticate
with it by issuing the command AUTH PLAIN followed by the
appropriate credentials.
$ telnet smtp.mandrillapp.com 25
Trying 54.204.65.134...
Connected to smtp.mandrillapp.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 smtp.mandrillapp.com ESMTP
ehlo test
250-ip-10-187-29-39
250-PIPELINING
250-SIZE 26214400
250-STARTTLS
250-AUTH PLAIN LOGIN
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250 8BITMIME
AUTH PLAIN AG1vb25wb22udEBob3RtYW2sLmNvbQBDaTMtY2RfOT0McklOd23OMFEsNGFB
235 2.7.0 Authentication successful
Mail From: testing@example.com
250 2.1.0 Ok
RCPT To: moonpoint@somesite.com
250 2.1.5 Ok
Data
354 End data with <CR><LF>.<CR><LF>
This is a test message.
.
250 2.0.0 Ok: queued as 85761C042C
quit
221 2.0.0 Bye
Connection closed by foreign host.
So what is that long string of characters after the AUTH
PLAIN command. That's actually the userid and password that the
server requires for authentication. It looks like just random letters
and numbers because the userid and password are
base64-encoded. You
can generate the encoded credentials using a Perl command similar to
the one below:
$ perl -MMIME::Base64 -e 'print encode_base64("\000moonpoint\@example.com\000SomePassword");'
AG1vb25wb2ludEBleGFtcGxlLmNvbQBTb21lUGFzc3dvcmQ=The command is in the format
perl -MMIME::Base64 -e
'print encode_base64("\000user_name\@domain_name\000Password");'.
The user name is preceded by \000, i.e., a backslash followed
by a null character represented by three zeros. If authentication requires
that you enter a userid in the form of userid@domainname, instead
of just username, then you need to precede the "@" with the
backslash escape
character. If you don't do so, Perl will think the "@" represents a
reference to an array and the result you get won't work.
You then add another backslash followed by three zeros and
the password. The encoded data will then be returned. In this case it was
AG1vb25wb2ludEBleGFtcGxlLmNvbQBTb21lUGFzc3dvcmQ= which is
what I would copy and paste after the AUTH PLAIN command when
providing credentials to the server. Note: you can also use online services
to do the base64 encoding, but you would be providing the login
credentials to get the results, so someone else could possibly learn the
userid and password.
References:
-
SMTP, testing via Telnet
Last modified: June 11, 2013
FreeBSDwiki
[/network/email]
permanent link
Thu, Apr 02, 2015 10:50 pm
Checking network errors with netstat -bI or -dI on OS X
You can determine the number of input packets and bytes and output
packets and byes on a network interface and check for errors on a
Mac OS X system using the command
netstat -bI interface
where
interface is a particular network interface
on the system, e.g., en0 or en1 or, alternatively, check all interfaces using
netstat -bi.
-b With the interface display (option -i, as described below), show the number of bytes
in and out.
-d With either interface display (option -i or an interval, as described below), show
the number of dropped packets.
-I interface
Show information about the specified interface; used with a wait interval as
described below. If the -s option is present, show per-interface protocol statis-
tics on the interface for the specified address_family or protocol, or for all pro-
tocol families.
-i Show the state of interfaces which have been auto-configured (interfaces statically
configured into a system, but not located at boot time are not shown). If the -a
options is also present, multicast addresses currently in use are shown for each
Ethernet interface and for each IP interface address. Multicast addresses are shown
on separate lines following the interface address with which they are associated.
If the -s option is present, show per-interface statistics on all interfaces for the
specified address_family or protocol, or for all protocol families.
E.g., using -bI to see information for particular
interfaces:
$ netstat -bI en0
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Ibytes Opkts Oerrs Obytes Coll
en0 1500 <Link#4> d4:9a:20:0d:e6:ec 0 0 0 0 0 836 0
$ netstat -bI en1
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Ibytes Opkts Oerrs Obytes Coll
en1 1500 <Link#5> f8:1e:df:d9:2b:64 22184840 0 13047081883 29605843 0 6652036717 0
en1 1500 gsod0009627 fe80:5::fa1e:dfff 22184840 - 13047081883 29605843 - 6652036717 -
en1 1500 192.168.3 192.168.3.4 22184840 - 13047081883 29605843 - 6652036717 -
Or -bi for all interfaces:
$ netstat -bi
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Ibytes Opkts Oerrs Obytes Coll
lo0 16384 <Link#1> 684926 0 46641907 684926 0 46641907 0
lo0 16384 localhost fe80:1::1 684926 - 46641907 684926 - 46641907 -
lo0 16384 127 localhost 684926 - 46641907 684926 - 46641907 -
lo0 16384 localhost ::1 684926 - 46641907 684926 - 46641907 -
gif0* 1280 <Link#2> 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
stf0* 1280 <Link#3> 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
en0 1500 <Link#4> d4:9a:20:0d:e6:ec 0 0 0 0 0 836 0
en1 1500 <Link#5> f8:1e:df:d9:2b:64 22186588 0 13047529007 29606897 0 6652193662 0
en1 1500 gsod0009627 fe80:5::fa1e:dfff 22186588 - 13047529007 29606897 - 6652193662 -
en1 1500 192.168.3 192.168.3.4 22186588 - 13047529007 29606897 - 6652193662 -
fw0 4078 <Link#6> d4:9a:20:ff:fe:0d:e6:ec 0 0 0 0 0 346 0
p2p0 2304 <Link#7> 0a:1e:df:d9:2b:64 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
vmnet 1500 <Link#9> 00:50:56:c0:00:01 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
vmnet 1500 192.168.49 192.168.49.1 0 - 0 0 - 0 -
vmnet 1500 <Link#10> 00:50:56:c0:00:08 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
vmnet 1500 172.16.79/24 172.16.79.1 0 - 0 0 - 0 -
utun0 1400 <Link#8> 4355 0 2689781 5506 10 2466553 0
utun0 1400 192.168.225.1 vpn-192-168-225 4355 - 2689781 5506 - 2466553 -
You can also use netstat -dI or netstat -di
to check for errors and dropped packets.
$ netstat -dI en1
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Opkts Oerrs Coll Drop
en1 1500 <Link#5> f8:1e:df:d9:2b:64 22188430 0 29608300 0 0
en1 1500 gsod0009627 fe80:5::fa1e:dfff 22188430 - 29608300 - - -
en1 1500 192.168.3 192.168.3.4 22188430 - 29608300 - - -
$ netstat -di
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Opkts Oerrs Coll Drop
lo0 16384 <Link#1> 685020 0 685020 0 0
lo0 16384 localhost fe80:1::1 685020 - 685020 - - -
lo0 16384 127 localhost 685020 - 685020 - - -
lo0 16384 localhost ::1 685020 - 685020 - - -
gif0* 1280 <Link#2> 0 0 0 0 0
stf0* 1280 <Link#3> 0 0 0 0 0
en0 1500 <Link#4> d4:9a:20:0d:e6:ec 0 0 0 0 0
en1 1500 <Link#5> f8:1e:df:d9:2b:64 22188931 0 29608571 0 0
en1 1500 gsod0009627 fe80:5::fa1e:dfff 22188931 - 29608571 - - -
en1 1500 192.168.3 192.168.3.4 22188931 - 29608571 - - -
fw0 4078 <Link#6> d4:9a:20:ff:fe:0d:e6:ec 0 0 0 0 0
p2p0 2304 <Link#7> 0a:1e:df:d9:2b:64 0 0 0 0 0
vmnet 1500 <Link#9> 00:50:56:c0:00:01 0 0 0 0 0
vmnet 1500 192.168.49 192.168.49.1 0 - 0 - - -
vmnet 1500 <Link#10> 00:50:56:c0:00:08 0 0 0 0 0
vmnet 1500 172.16.79/24 172.16.79.1 0 - 0 - - -
utun0 1400 <Link#8> 5088 0 6597 10 0
utun0 1400 192.168.225.1 vpn-192-168-225 5088 - 6597 - - -
If you would like comprehensive per-protocol statisitics for TCP,
UDP, and ICMP, you can use netstat -s.
-s Show per-protocol statistics. If this option is repeated, counters with a value of
zero are suppressed.
E.g.:
$ netstat -s
tcp:
29261464 packets sent
17057982 data packets (1342507929 bytes)
25181 data packets (11210523 bytes) retransmitted
0 resends initiated by MTU discovery
10449225 ack-only packets (7938 delayed)
0 URG only packets
508 window probe packets
767946 window update packets
961091 control packets
0 data packets sent after flow control
21404953 packets received
8137595 acks (for 1341998962 bytes)
377994 duplicate acks
0 acks for unsent data
13805067 packets (1284085790 bytes) received in-sequence
14783 completely duplicate packets (8462565 bytes)
69 old duplicate packets
83 packets with some dup. data (50503 bytes duped)
126989 out-of-order packets (165558655 bytes)
108 packets (126046 bytes) of data after window
18 window probes
3196 window update packets
10932 packets received after close
13 bad resets
0 discarded for bad checksums
0 discarded for bad header offset fields
0 discarded because packet too short
697585 connection requests
825 connection accepts
9 bad connection attempts
0 listen queue overflows
265086 connections established (including accepts)
700724 connections closed (including 167300 drops)
4971 connections updated cached RTT on close
4971 connections updated cached RTT variance on close
2672 connections updated cached ssthresh on close
64419 embryonic connections dropped
4638680 segments updated rtt (of 4788660 attempts)
3759189 retransmit timeouts
3379 connections dropped by rexmit timeout
0 connections dropped after retransmitting FIN
1219 persist timeouts
6 connections dropped by persist timeout
261605 keepalive timeouts
200056 keepalive probes sent
55755 connections dropped by keepalive
4620911 correct ACK header predictions
12309843 correct data packet header predictions
15932 SACK recovery episodes
3124 segment rexmits in SACK recovery episodes
3960674 byte rexmits in SACK recovery episodes
31573 SACK options (SACK blocks) received
124018 SACK options (SACK blocks) sent
0 SACK scoreboard overflow
udp:
2731040 datagrams received
0 with incomplete header
0 with bad data length field
0 with bad checksum
127081 dropped due to no socket
692901 broadcast/multicast datagrams dropped due to no socket
1 dropped due to full socket buffers
0 not for hashed pcb
1911057 delivered
18196924 datagrams output
ip:
27677449 total packets received
0 bad header checksums
0 with size smaller than minimum
0 with data size < data length
0 with ip length > max ip packet size
0 with header length < data size
0 with data length < header length
0 with bad options
0 with incorrect version number
443 fragments received
0 fragments dropped (dup or out of space)
0 fragments dropped after timeout
141 packets reassembled ok
24114721 packets for this host
11749 packets for unknown/unsupported protocol
0 packets forwarded (0 packets fast forwarded)
805 packets not forwardable
3549872 packets received for unknown multicast group
0 redirects sent
47854947 packets sent from this host
101 packets sent with fabricated ip header
0 output packets dropped due to no bufs, etc.
11620 output packets discarded due to no route
51 output datagrams fragmented
102 fragments created
0 datagrams that can't be fragmented
0 tunneling packets that can't find gif
130 datagrams with bad address in header
0 packets dropped due to no bufs for control data
icmp:
127081 calls to icmp_error
0 errors not generated 'cuz old message was icmp
Output histogram:
echo reply: 340
destination unreachable: 127081
0 messages with bad code fields
0 messages < minimum length
0 bad checksums
0 messages with bad length
0 multicast echo requests ignored
0 multicast timestamp requests ignored
Input histogram:
echo reply: 639
destination unreachable: 7646
routing redirect: 2468
echo: 340
time exceeded: 136
time stamp: 17
information request: 2
address mask request: 17
UDP: 5
340 message responses generated
ICMP address mask responses are disabled
igmp:
11768 messages received
0 messages received with too few bytes
30 messages received with wrong TTL
0 messages received with bad checksum
11676 V1/V2 membership queries received
29 V3 membership queries received
0 membership queries received with invalid field(s)
11705 general queries received
0 group queries received
0 group-source queries received
0 group-source queries dropped
32 membership reports received
0 membership reports received with invalid field(s)
32 membership reports received for groups to which we belong
0 V3 reports received without Router Alert
11118 membership reports sent
ipsec:
0 inbound packets processed successfully
0 inbound packets violated process security policy
0 inbound packets with no SA available
0 invalid inbound packets
0 inbound packets failed due to insufficient memory
0 inbound packets failed getting SPI
0 inbound packets failed on AH replay check
0 inbound packets failed on ESP replay check
0 inbound packets considered authentic
0 inbound packets failed on authentication
0 outbound packets processed successfully
0 outbound packets violated process security policy
0 outbound packets with no SA available
0 invalid outbound packets
0 outbound packets failed due to insufficient memory
0 outbound packets with no route
ip6:
467000 total packets received
0 with size smaller than minimum
0 with data size < data length
0 with bad options
0 with incorrect version number
94 fragments received
0 fragments dropped (dup or out of space)
1 fragment dropped after timeout
0 fragments that exceeded limit
35 packets reassembled ok
32768 packets for this host
0 packets forwarded
415268 packets not forwardable
0 redirects sent
10803 packets sent from this host
0 packets sent with fabricated ip header
0 output packets dropped due to no bufs, etc.
48739 output packets discarded due to no route
1025 output datagrams fragmented
2050 fragments created
0 datagrams that can't be fragmented
0 packets that violated scope rules
415268 multicast packets which we don't join
Input histogram:
hop by hop: 30801
TCP: 10
UDP: 422348
fragment: 94
ICMP6: 13747
Mbuf statistics:
10 one mbuf
two or more mbuf:
lo0= 9624
457366 one ext mbuf
0 two or more ext mbuf
0 packets whose headers are not continuous
0 tunneling packets that can't find gif
0 packets discarded due to too may headers
0 failures of source address selection
0 forward cache hit
0 forward cache miss
0 packets dropped due to no bufs for control data
icmp6:
0 calls to icmp_error
0 errors not generated because old message was icmp error or so
0 errors not generated because rate limitation
Output histogram:
router solicitation: 443
neighbor solicitation: 171
neighbor advertisement: 133
MLDv2 listener report: 377
0 messages with bad code fields
0 messages < minimum length
0 bad checksums
0 messages with bad length
Input histogram:
multicast listener query: 11644
MLDv1 listener report: 23
neighbor solicitation: 7
neighbor advertisement: 7290
Histogram of error messages to be generated:
0 no route
0 administratively prohibited
0 beyond scope
0 address unreachable
0 port unreachable
0 packet too big
0 time exceed transit
0 time exceed reassembly
0 erroneous header field
0 unrecognized next header
0 unrecognized option
0 redirect
0 unknown
0 message responses generated
0 messages with too many ND options
0 messages with bad ND options
0 bad neighbor solicitation messages
0 bad neighbor advertisement messages
0 bad router solicitation messages
0 bad router advertisement messages
0 bad redirect messages
0 path MTU changes
ipsec6:
0 inbound packets processed successfully
0 inbound packets violated process security policy
0 inbound packets with no SA available
0 invalid inbound packets
0 inbound packets failed due to insufficient memory
0 inbound packets failed getting SPI
0 inbound packets failed on AH replay check
0 inbound packets failed on ESP replay check
0 inbound packets considered authentic
0 inbound packets failed on authentication
0 outbound packets processed successfully
0 outbound packets violated process security policy
0 outbound packets with no SA available
0 invalid outbound packets
0 outbound packets failed due to insufficient memory
0 outbound packets with no route
rip6:
0 messages received
0 checksum calcurations on inbound
0 messages with bad checksum
0 messages dropped due to no socket
0 multicast messages dropped due to no socket
0 messages dropped due to full socket buffers
0 delivered
0 datagrams output
pfkey:
242 requests sent to userland
3872 bytes sent to userland
histogram by message type:
register: 122
flush: 60
x_spdflush: 60
0 messages with invalid length field
0 messages with invalid version field
0 messages with invalid message type field
0 messages too short
0 messages with memory allocation failure
0 messages with duplicate extension
0 messages with invalid extension type
0 messages with invalid sa type
0 messages with invalid address extension
242 requests sent from userland
14064 bytes sent from userland
histogram by message type:
register: 122
flush: 60
x_spdflush: 60
0 messages toward single socket
120 messages toward all sockets
60 messages toward registered sockets
0 messages with memory allocation failure
You can have the display of counters with a value of zero omitted using
the options -ss, instead of -s. E.g.:
$ netstat -ss
tcp:
29262147 packets sent
17058355 data packets (1342573989 bytes)
25181 data packets (11210523 bytes) retransmitted
10449497 ack-only packets (7938 delayed)
508 window probe packets
767946 window update packets
961129 control packets
21405439 packets received
8137921 acks (for 1342065132 bytes)
378012 duplicate acks
13805277 packets (1284149452 bytes) received in-sequence
14785 completely duplicate packets (8462978 bytes)
69 old duplicate packets
83 packets with some dup. data (50503 bytes duped)
126989 out-of-order packets (165558655 bytes)
108 packets (126046 bytes) of data after window
18 window probes
3196 window update packets
10932 packets received after close
13 bad resets
697607 connection requests
825 connection accepts
9 bad connection attempts
265103 connections established (including accepts)
700745 connections closed (including 167300 drops)
4971 connections updated cached RTT on close
4971 connections updated cached RTT variance on close
2672 connections updated cached ssthresh on close
64422 embryonic connections dropped
4638941 segments updated rtt (of 4788924 attempts)
3759239 retransmit timeouts
3379 connections dropped by rexmit timeout
1219 persist timeouts
6 connections dropped by persist timeout
261618 keepalive timeouts
200066 keepalive probes sent
55758 connections dropped by keepalive
4621122 correct ACK header predictions
12309982 correct data packet header predictions
15932 SACK recovery episodes
3124 segment rexmits in SACK recovery episodes
3960674 byte rexmits in SACK recovery episodes
31573 SACK options (SACK blocks) received
124018 SACK options (SACK blocks) sent
udp:
2731110 datagrams received
127082 dropped due to no socket
692942 broadcast/multicast datagrams dropped due to no socket
1 dropped due to full socket buffers
1911085 delivered
18197031 datagrams output
ip:
27678514 total packets received
443 fragments received
141 packets reassembled ok
24115277 packets for this host
11749 packets for unknown/unsupported protocol
805 packets not forwardable
3550381 packets received for unknown multicast group
47855748 packets sent from this host
101 packets sent with fabricated ip header
11620 output packets discarded due to no route
51 output datagrams fragmented
102 fragments created
130 datagrams with bad address in header
icmp:
127082 calls to icmp_error
Output histogram:
echo reply: 340
destination unreachable: 127082
Input histogram:
echo reply: 639
destination unreachable: 7646
routing redirect: 2468
echo: 340
time exceeded: 136
time stamp: 17
information request: 2
address mask request: 17
UDP: 5
340 message responses generated
ICMP address mask responses are disabled
igmp:
11768 messages received
30 messages received with wrong TTL
11676 V1/V2 membership queries received
29 V3 membership queries received
11705 general queries received
32 membership reports received
32 membership reports received for groups to which we belong
11118 membership reports sent
ipsec:
ip6:
467000 total packets received
94 fragments received
1 fragment dropped after timeout
35 packets reassembled ok
32768 packets for this host
415268 packets not forwardable
10803 packets sent from this host
48739 output packets discarded due to no route
1025 output datagrams fragmented
2050 fragments created
415268 multicast packets which we don't join
Input histogram:
hop by hop: 30801
TCP: 10
UDP: 422348
fragment: 94
ICMP6: 13747
Mbuf statistics:
10 one mbuf
two or more mbuf:
lo0= 9624
457366 one ext mbuf
0 two or more ext mbuf
icmp6:
Output histogram:
router solicitation: 443
neighbor solicitation: 171
neighbor advertisement: 133
MLDv2 listener report: 377
Input histogram:
multicast listener query: 11644
MLDv1 listener report: 23
neighbor solicitation: 7
neighbor advertisement: 7290
Histogram of error messages to be generated:
0 no route
0 administratively prohibited
0 beyond scope
0 address unreachable
0 port unreachable
0 packet too big
0 time exceed transit
0 time exceed reassembly
0 erroneous header field
0 unrecognized next header
0 unrecognized option
0 redirect
0 unknown
ipsec6:
rip6:
pfkey:
242 requests sent to userland
3872 bytes sent to userland
histogram by message type:
register: 122
flush: 60
x_spdflush: 60
242 requests sent from userland
14064 bytes sent from userland
histogram by message type:
register: 122
flush: 60
x_spdflush: 60
120 messages toward all sockets
60 messages toward registered sockets
[/os/os-x]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact











