←February→
| Sun |
Mon |
Tue |
Wed |
Thu |
Fri |
Sat |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
| 2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
| 9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
| 16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
| 23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
|
|
|
Fri, Feb 28, 2014 10:41 pm
Using awk to sum numbers in a file
The awk command found on Linux/Unix and Mac OS X systems can be used to
sum numbers in a file. E.g., suppose the file
numbers.txt
contains the following numbers:
10
20
30
40
50
1
2
3
4
5
The contents of the file can be piped into the awk command with
the cat command and then summed by awk.
$ cat numbers.txt | awk '{sum+=$1} END {print sum}'
165If the numbers are not in the first column in the file, but were in the
second column instead, you can adjust $1 to be the relevant
column instead. E.g, if the file contents looked like the following with
the numbers in the second column, then you would use $2 instead.
Dave 10
Bill 20
Joe 30
Mary 40
Maria 50
Howard 1
Sam 2
Lisa 3
Karen 4
Nina 5
$ cat numbers.txt | awk '{sum+=$2} END {print sum}'
165If you know the numbers always occur in specific colum positions in the file,
e.g., in positions 10 to 15, you could also use the cut
command instead of the cat command. E.g., if you file contained:
Dave 10
Bill 20
Joe 30
Mary 40
Maria 50
Howard 1
Sam 2
Lisa 3
Karen 4
Nina 5
$ cut -c10-11 numbers.txt | awk '{sum+=$1} END {print sum}'
165
[/os/unix/commands]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 28, 2014 10:09 pm
Managing Wi-Fi from the terminal command line under OS X
To manage
Wi-Fi connections from a shell prompt on a Mac OS X system you can
obtain a command line interface by running the
Terminal program located
in Applications/Utilities. From that command line interface, you can determine
whether a WiFi interface is present on the system using the command
networksetup -listallnetworkservices. You should see "Wi-Fi"
in the list of services that appears when you issue the command.
$ networksetup -listallnetworkservices
An asterisk (*) denotes that a network service is disabled.
Bluetooth DUN
Ethernet
FireWire
Wi-Fi
To determine the hardware interface supporting Wi-Fi connections you
can use the command networksetup -listallhardwareports.
$ networksetup -listallhardwareports
Hardware Port: Bluetooth DUN
Device: Bluetooth-Modem
Ethernet Address: N/A
Hardware Port: Ethernet
Device: en0
Ethernet Address: d4:9a:20:0d:e6:ec
Hardware Port: FireWire
Device: fw0
Ethernet Address: d4:9a:20:ff:fe:0d:e6:ec
Hardware Port: Wi-Fi
Device: en1
Ethernet Address: f8:1e:df:d9:2b:66
VLAN Configurations
===================
In the case above, the Wi-Fi interface is en1.
To get information on the status of the system's Wi-Fi connection, you
can use the command networksetup -getinfo Wi-Fi.
$ networksetup -getinfo Wi-Fi
DHCP Configuration
IP address: 192.168.0.5
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Router: 192.168.0.1
Client ID:
IPv6: Automatic
IPv6 IP address: none
IPv6 Router: none
Wi-Fi ID: f8:1e:df:d9:2b:66
To find if the system is currently connected to a wireless network and the
network name for the current wireless connection, you can use
networksetup -getairportnetwork <device name> where
device name is the network interface on the system that supports
WiFi connections. E.g.:
$ networksetup -getairportnetwork en1
Current Wi-Fi Network: Copernicus
If you stipulate a network interface that is not a WiFi interface, you
will get an error message indicating the interface is not a Wi-Fi interface
as shown below:
$ networksetup -getairportnetwork en0
en0 is not a Wi-Fi interface.
** Error: Error obtaining wireless information.
If you wish to to turn the Wi-Fi connection on or off from a shell
prompt, you can use the networksetup -setairportnetwork
command.
networksetup -setairportnetwork <device name> <network> [password]
$ networksetup -setairportpower en1 off
$ networksetup -getairportnetwork en1
You are not associated with an AirPort network.
Wi-Fi power is currently off.
$ networksetup -setairportpower en1 on
$ networksetup -getairportnetwork en1
Current Wi-Fi Network: Copernicus
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Thu, Feb 27, 2014 10:13 pm
Determining available WiFi networks from OS X shell prompt
On a Mac OS X system, such as a MacBook Pro laptop, you can detemine the
available WiFi networks from a shell prompt, which you can get by running
the
Terminal program located in
Applications/Utilities,
by using the command below:
/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/A/Resources/airport scan
For example:
$ /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/A/Resources/airport scan
SSID BSSID RSSI CHANNEL HT CC SECURITY (auth/unicast/group)
SC8QR f8:e4:fb:ea:29:5d -86 11 Y -- WPA2(PSK/AES,TKIP/TKIP)
08FX02038916 00:18:3a:8a:01:c5 -80 6 N -- WEP
Norman Netgear 84:1b:5e:2d:c9:16 -79 6 Y -- WPA2(PSK/AES/AES)
558935 0c:54:a5:48:19:e5 -16 1 Y -- WPA(PSK/AES,TKIP/TKIP) WPA2(PSK/AES,TKIP/TKIP)
Hickox 0c:d5:02:c5:e8:8e -80 11 N -- WEP
Haze 94:44:52:5a:54:54 -33 11 Y -- WPA(PSK/AES/AES) WPA2(PSK/AES/AES)
David's Net ec:1a:59:8d:dd:61 -80 11 Y -- WPA2(PSK/AES/AES)
The
SSID is the "Service Set Identification", which is a 1 to 32 byte string
that represents the "network name". The SSID allows you to identify a network
to which you may wish to connect. Sometimes a person setting up a wireless
router may choose to not have the SSID broadcast. In that case you wouldn't
see the SSID in the list even though the network is available for connections
if you know the SSID.
The
BSSID is the "Basic Service Set Identification". Each Basic Service Set is
identified by a BSSID. For a BSS operating in infrastructure mode, the BSSID
is the media access control
(MAC) address of the
wireless access
point (WAP), which is generated by combining the 24-bit
Organizationally Unique Identifier, which identifies the manufacturer,
and the manufacturer's assigned 24-bit identifier for the radio
chipset in the WAP. The BSSID is the formal name of the BSS and is
always associated with only one BSS. The SSID is the informal human
name of the BSS which is more easily remembered by humans.
You can determine the manufacturer from the BSSID by searching the
IEE-SA - Registration Authority MA-L Public Listing. Take the first six
digits of the BSSID and replace the colons with dashes and then put the
result, which will be in the form of xx-xx-xx in the "Search for" field. E.g.,
in the case of the wireless network above identified as "David's Net", the
BSSID is ec:1a:59:8d:dd:61, so you would search using
ec-1a-59, which would show the wireless device was
manufacturered by Belkin International Inc., a company that make wireless
routers for the home market. For the network identified as "Norman Netgear",
searching on 84-1b-5e shows the manufacturer is, indeed, Netgear.
If you just want the names of the available networks, i.e., the SSIDs, you
can use the same command and then pipe its output to the cut command. Since
the SSID will be the first 32 characters on each line, you will need to cut
out the first 32 characters from each line.
$ /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/A/Resources/airport scan | cut -c1-32
SSID
SC8QR
08FX02038916
Norman Netgear
558935
Hickox
Haze
David's Net
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Wed, Feb 26, 2014 5:50 pm
MSYS
If you would like to be able to use Unix/Linux utilities such as
awk, cut, grep, less, sed, sort, tail, wc, etc. on a Microsoft Windows
system,
MSYS provides these and
many other
GNU utilities
for Microsoft Windows systems.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/software/utilities]
permanent link
Sun, Feb 23, 2014 1:37 pm
Accessing Deleted Wikipedia Pages
Wikipedia pages can be edited by anyone; they can also be deleted
entirely by Wikipedia administrators for a variety of reasons. Within
the Wikipedia community there are differing views regarding the
retention and deletion of articles, e.g., see the Wikipedia article
Deletionism and inclusionism in Wikipedia. If you read an article
and want to ensure you have access to the information in the future, the
best course is probably to use Wikipedia's own "print/export" feature or
to save the content of the article elsewhere by using a service such as
Evernote, which provides notetaking
and webpage archiving services,
Diigo,
which provides a social bookmarking service with the capability to store
a copy of webpages you have visited, i.e., to "cache" them so that you
can view the webpage again as it was when it was cached whether it has
been changed or deleted in the interim, or similar services. But, if
you haven't archived an article and find a Wikipedia page was deleted and
so is inaccessible to you, there are still some options available to you.
If the article was deleted some time between February and September 2008, you may be able to find it on
Deletionpedia at
deletionpedia.dbatley.com
Deletionpedia is an archive that contains 62,224 pages which were deleted from
the English-language Wikipedia between February and September 2008.
If you know the title of the article that was deleted, you can browse
"Pages
deleted after more than 1000 days on Wikipedia" or
"
Pages edited more than 200 times" by their alphabetical listings. If you
know the date the article was deleted which, if you have the Wikipedia URL for the article, can be found
by visiting the URL for the article on Wikipedia, you can find it by
searching Deletionpedia by
Pages by deletion date.
Deletionpdedia's own search feature is disabled and the
site suggests you use Google to search Deletionpedia. However,
I've found that approach is likely to miss articles stored
on Deletionpedia. E.g., Deletionpedia contains the article
Elvis sightings (deleted 03 Jul 2008 at 10:12),
yet if you search the site using Google with Elvis
sightings site:deletionpedia.dbatley.com, no results
are returned. Incidentally, Wikipedia does now contain an Elvis sightings
article.
Interestingly, though Wikipedia now contains a
Deletionpedia article, that article was itself
once deleted from Wikipedia.
Another site Fixed Reference: Snapshots
of Wikipedia provides access to articles archived in April and July of 2004.
Because Fixed Reference and Deletionpedia only provide access to articles from
two years, 2004 for Fixed Reference and 2008 for Deletionpedia, their usefulness
for accessing deleted articles is very limited.
Another alternative is to search the
Internet
Archive at archive.org. The Internet
Archive is a non-profit digital library with the stated mission of
"universal access to all knowledge." It also archives pages found on
the World Wide Web
(WWW). The archived pages, which are created for a website when the Internet
Arhive periodically scans the site, are accessible through its
Wayback Machine.
The name is a reference to the time machine used by Mr. Peabody, a talking dog,
and his human companion, Sherman, in the cartoon series
The Rocky and Bullwinkle Show to visit famous
events in history. You can choose to "Browse History" to search for an
archived copy of the page deleted from Wikipedia, if you know its URL.
If the page was archived by the Internet Archive multiple times over a period
of time, which could span years, you can view the page as it was on the
particular days it was archived.
Another place you can check for deleted Wikipedia pages or pages that
have disappeared from any website is
Archive.is, which aims to be "your personal Wayback Machine!" The site
can be freely used by anyone to take a "snapshot" of a webpage that will
always be online even if the original page disappears. So, if someone else
has archived a particular webpage for which you are searching, you may find
it at Archive.is. You can also use the
site to archive pages you may want to access later that could disappear from
the original site or to make the pages available should the original site
disappear from the web.
[/reference]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 08, 2014 10:31 pm
ToDoList
I needed software that I could run on a system running Microsoft Windows
8 to help me manage projects and tasks. I had been using an online service
for awhile, but was looking for software I could run on the system that
would give me some additional capabilities, but I didn't want to spend
several hundred dollars on Microsoft Project, which, though it offers all
the features I might need, is overkill for my current needs. I found
ToDoList, which
is free to be an easy program to quickly start managing my projects and tasks.
[
More Info ]
[/software/projmgmt]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 08, 2014 5:27 pm
KPT Plugins and Corel Paintshop Pro X6
The Corel
PaintShop
Pro program supports a number of plugins that provide special effects
for images. For the X6 version of PaintShop Pro, Corel provides both 32-bit
and 64-bit versions of the software. However, the
Kai's Power Tools
(KPT) plugins will only work with the 32-bit version as the plugins are
incompatible with the 64-bit version.
Kai's Power Tools (KPT) was developed by
Kai Krause, but sold
to Corel Corporation
. Kai also developed Live Picture, Bryce, Kai's Power Show, Kai's
Power Goo, Convolver, Kai's Photo Soap and
Poser. He pioneered user
interface elements in his software such as soft shadows, rounded corners, and
translucency.
References:
-
Is the Paintshop Pro X6 KPT Collection Compatible with the 64 Bit version of
Paintshop Pro X6?
Corel Discovery Center
[/os/windows/software/graphics/corel/psp]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 07, 2014 8:55 pm
Determine the date of manufacture of a Mac system
On my MacBook Pro laptop, running OS X 10.8.3, I can see the date it was
manufactured by clicking on the Apple icon in the upper-left corner of
the screen then selecting
About This Mac and then clicking on
the
More Info... button.
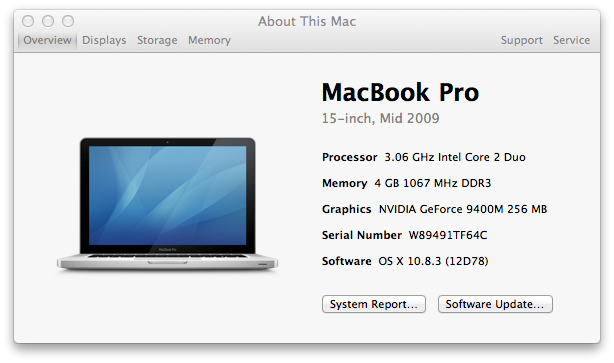
If you need to get the information from a command line interface, e.g., from
a terminal or SSH session, you can't get it directly using the
system_profiler command, but you can use information provided
by that command to look up the information online.
$ system_profiler SPHardwareDataType
Hardware:
Hardware Overview:
Model Name: MacBook Pro
Model Identifier: MacBookPro5,3
Processor Name: Intel Core 2 Duo
Processor Speed: 3.06 GHz
Number of Processors: 1
Total Number of Cores: 2
L2 Cache: 6 MB
Memory: 4 GB
Bus Speed: 1.07 GHz
Boot ROM Version: MBP53.00AC.B03
SMC Version (system): 1.48f2
Serial Number (system): W89491TF64C
Hardware UUID: FDE9B14D-E531-569F-A1EF-D0D0D0D0D0D0
Sudden Motion Sensor:
State: EnabledYou can use the model identifier information to look up information on
when the model was manufactured using
Lookup Mac Specs by
Serial Number, Order, Model, & EMC Number, Model ID @ EveryMac.com.
If you just want the model identifier, you can use awk
to isolate that information.
$ system_profiler SPHardwareDataType | awk '/Model Identifier/ {print $3}'
MacBookPro5,3When I looked up MacBookPro5,3, I saw 3 entries with
a "subfamily" of Mid-2009 15" listed for each. All 3 were
introduced on June 8, 2009 and discontinued on April 13, 2010. Using the
processor speed information provided by system_profiler, I
could narrow the selection down to a specific MacBook Pro "Core 2 Duo" and
see the standard RAM and hard disk size for that model.
You can also enter the last 3 characters of a 11 character serial
number to obtain that information from the site. Though, in my case
I saw an iPhone and several desktop systems listed as well as one
laptop model, though, since I knew it was a laptop, I knew which one
was the appropriate one.
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Wed, Feb 05, 2014 12:01 pm
Using the control key to select multiple items with IE under VMWare
If you need to select multiple items on a form on a webpage in Internet
Explorer on a Microsoft Windows system, you can usually do so by holding
down the Ctrl key while selecting the items. On an Apple keyboard, though,
there is no Ctrl key though there is a Control key. But if you are using
VMWare Fusion to
run a version of Microsoft Windows in a
virtual machine (VM)
on a Mac OS X system, you can't use that Control key to select multiple items
on a form when you are using Internet Explorer in the VM unless you change
the default keyboard configuration, which can easily be done by taking the
following steps:
-
Click on VMWare Fusion at the top left of the VMWare window.
-
Select "Preferences".
-
Select "Keyboard & Mouse".
-
Click on the "Mouse Shortcuts" tab.
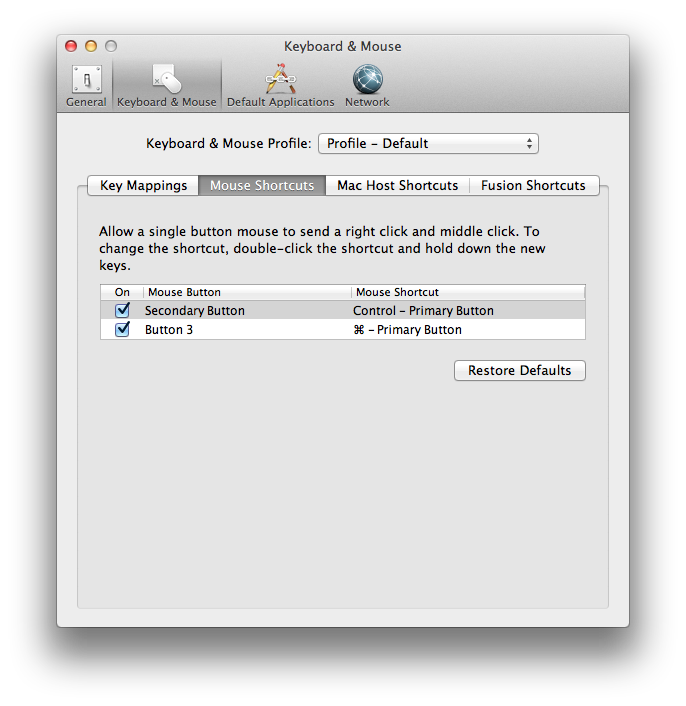
-
Uncheck "Secondary Button"; you can then close the "Keyboard & Mouse"
window.
You can then select multiple items on a form by holding down the Control key
while left clicking on items. If you want to go back to the default
configuration afterwards, you can go back to the "Mouse Shortcuts"
tab and click on the "Restore Defaults" button or just recheck the
"Secondary Button" checkbox, which is associated with the mouse shortcut
"Control - Primary Button".
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Sun, Feb 02, 2014 10:02 pm
32 or 64-bit Application
If you need to determine whether a Microsoft Windows application is a
32-bit or 64-bit program, there are a number of ways to do so, including
simply right-clicking on the file and examining its properties.
[
More Info ]
[/os/windows]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact




