←March→
| Sun |
Mon |
Tue |
Wed |
Thu |
Fri |
Sat |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
| 8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
| 15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
| 22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
| 29 |
30 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thu, Feb 26, 2026 10:31 pm
Restarting the Windows audio service
If you are experiencing problems with sound on a Microsoft Windows system,
such as being unable to hear audio even when the sound hasn't been muted
and any external speakers are turned on and set to an audible volume level,
one possible way to resolve the problem is to restart the
Windows Audio service. To do so, you can can take the following steps:
- Type
services in
the Windows Search field. You should see it returned by the search
utility. Click on "Run as administrator" and provide the login credentials
for an account that has adminisrator privileges.
- When the Services window opens, scroll
down until you see Windows Audio.
- Right-click on the entry and choose "Restart".
- When the status for the service returns to "Running",
you can close the Services window.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows]
permanent link
Mon, Feb 23, 2026 10:05 pm
Determining if a drive is encrypted with Bitlocker on a Windows system
If you need to determine if a drive in a Microsoft Windows system or connected
to it via USB is
BitLocker encrypted, you
can use the
manage-bde utility. To use the program, open a
command prompt window with
administrator privileges and then issue the command
manage-bde -status to see the status of all drives. To see just
the status of one drive, e.g., C:, you could use manage-bde -status
C:.
C:\Windows\System32>manage-bde -status c:
BitLocker Drive Encryption: Configuration Tool version 10.0.26100
Copyright (C) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Volume C: [Windows]
[OS Volume]
Size: 14826.87 GB
BitLocker Version: None
Conversion Status: Fully Decrypted
Percentage Encrypted: 0.0%
Encryption Method: None
Protection Status: Protection Off
Lock Status: Unlocked
Identification Field: None
Key Protectors: None Found
C:\Windows\System32>
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/commands]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 14, 2026 7:02 pm
Changing the time zone on a Microsoft Windows system from the command line
The timezone on a Microsoft Windows system can be changed from the
command line
by
opening a command prompt window
with administrator privileges and then typing
timedate.cpl and
hitting
Enter, which opens a window where you can alter the
timezone or you can use the
tzutil utility to
change the time zone using a command of the form
tzutil /s
"TimeZone" where
TimeZone is the appropriate time zone
identifier, e.g.,
tzutil /s "Eastern Standard Time".
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/commands]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 13, 2026 9:45 pm
Installing OpenSSH Server software on a Windows 10 system with PowerShell
OpenSSH Server for
Windows 10 requires at
least Windows 10 (build 1809).
You can determine the build number for Windows 10 by typing winver
in the Windows "Type here to search" field at the bottom of the screen or
at a
PowerShell prompt. Or
you can use the
systeminfo utility and pipe it's output into the
findstr command, filtering
on the line that has "OS" at the beginning of the line and also "Version" in
the line.
PS C:\> systeminfo | findstr -B "OS" | findstr "Version"
OS Version: 10.0.19045 N/A Build 19045
PS C:\>
The SSH Client software may already be installed. You can determine if
it is already installed by opening a PowerShell prompt and typing
ssh. If it is installed, as it was on the Windows 10 Professional
Version 22H2 (OS Build 19045.6466) system on which I wanted to set up
the OpenSSH Server software, you will see a response like the following one:
PS C:\> ssh
usage: ssh [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-B bind_interface] [-b bind_address]
[-c cipher_spec] [-D [bind_address:]port] [-E log_file]
[-e escape_char] [-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-i identity_file]
[-J destination] [-L address] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec]
[-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-P tag] [-p port] [-Q query_option]
[-R address] [-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-w local_tun[:remote_tun]]
destination [command [argument ...]]
PS C:\>[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/network/ssh/OpenSSH]
permanent link
Mon, Nov 24, 2025 7:46 pm
Determining the location of a user's "My Documents" folder with PowerShell
I needed to move some files from one Windows 11 system that is no longer
being used, as the user is no longer working for the company, to another
Windows 11 system where the user of that system, Pam, is now handling a task
formerly handled by the prior employee, but while logged onto the account for
the user now handling the task on her system, I noticed that her
Documents folder was empty. The
Windows domain name
changed at that business a few years ago, so I thought that perhaps she
might be using a Documents directory associated with her account under
the prior domain name rather than the new one created for her new domain
login. You can determine the location of a user's "My Documents" directory,
which can be redirected to another location, including a network share
or another drive, by issuing the PowerShell command
[Environment]::GetFolderPath("MyDocuments"). E.g.:
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6
PS C:\Users\Pam> [Environment]::GetFolderPath("MyDocuments")
C:\Users\Pam\Documents
PS C:\Users\Pam>The command utilizes the GetFolderPath method from the
System.Environment class to retrieve the path of special folders,
including "MyDocuments," for the user under whose context the script or command
is executed. This method correctly identifies the mapped location even if the
Documents folder has been redirected or moved from the default location.
In this case, I found that her "My Documents" directory was pointing to
the directory associated with the old domain name. Her "home" folder
was also pointing to the home folder that was in use for her account
in the old domain. You can type $home in a PowerShell window to
see that value. Or you can use $env:USERPROFILE to see the same
information.
PS C:\Users\Pam> $Home
C:\Users\Pam
PS C:\Users\Pam >$env:userprofile
C:\Users\Pam
PS C:\Users\Pam>
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Sat, Nov 22, 2025 10:12 pm
PowerShell cmdlets to check remote connectivity and firewall rules
When I tried to establish a
Secure Shell (SSH)
connection to a Windows 11 PC at a remote location today, I was unable to
do so. I usually connect to the
Windows
domain controller at the location and establish the SSH connection
to the user's Windows 11 system through it, but that was not working. I thought
the problem was likely due to
McAfee stopping providing
firewall protection for incoming connections to ports on PCs as part of
their antivirus software, since the antivirus
software on PCs at that location was
McAfee Antivirus
Plus. When McAfee stopped providing that firewall service as part of
McAfee AntiVirus Plus, the software reverted firewall protection for incoming
connections to Microsoft's default firewall software,
Microsoft Defender
Firewall, aka Windows Firewall. When I check firewall protection on a
Windows system running McAfee AntiVirus Plus, I now see the following message:
McAfee and Windows Defender are now working side by side
Our Advanced Firewall provides enhanced protection by blocking risky
outgoing connections. Windows Defender Firewall provides protection for
incoming connections.
Keep both firewalls on for complete protection.
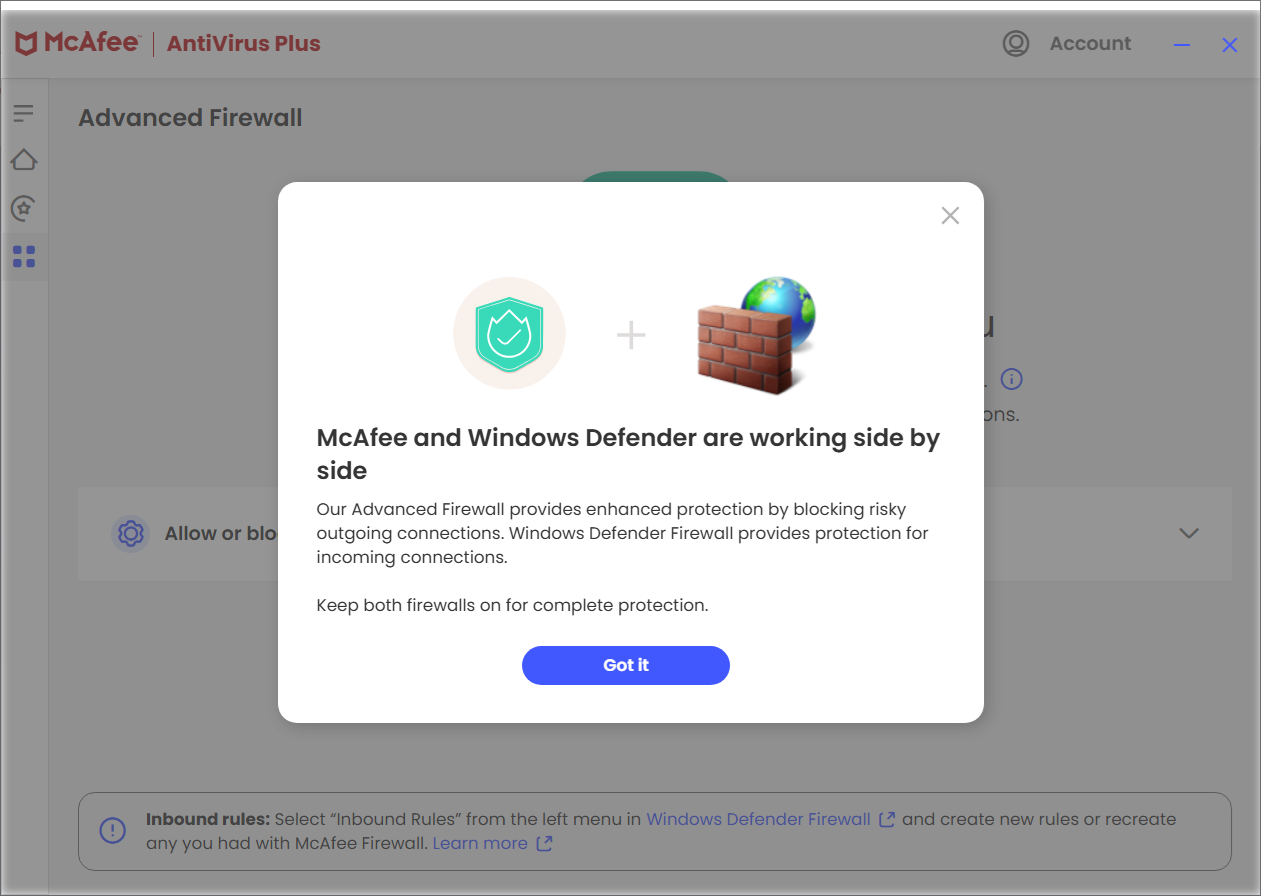
So I thought I likely needed to create similar firewall rules for
incoming connections in the Windows Firewall software as had existed
previously in the McAfee firewall software.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Sun, Jun 01, 2025 8:13 pm
Installing the Microsoft-provided SSH server software on a Windows 11 system
Microsoft provides
Secure Shell (SSH)
server software with Windows 11 that you can use to listen for connections
from remote SSH clients, but the server service is not installed by default.
To install the Microsoft-provided SSH server software on a Windows 11 system,
take the following steps:
-
Type optional features in the Windows Search field at the
bottom of the screen and hit Enter, then click on "Open" when it is
found.
-
Click on the View features button.
-
Scroll down the list of optional features until you see
Open SSH Server and then click on the check box for it
and click on the Next button.
-
Click on the Add button to add the OpenSSH Server capability
to the system.
-
When the Optional features window shows that the OpenSSH Server
software has been added, you can close the window.
If you scroll down the list of added features before closing the
window, you should see OpenSSH Server below OpenSSH Client.
After installing the software, you will need to start the OpenSSH server
service.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/network/ssh/OpenSSH]
permanent link
Sun, Mar 09, 2025 9:53 pm
Creating a bootable USB flash drive from an ISO file using Rufus
If you have an
ISO
file that could be written to a CD or DVD to boot a system, but wish to
use it to create a bootable
USB
flash drive and
wish to do so using software on a Microsoft Windows system, you
can use
Rufus.
The developer is Pete Batard and his blog can be found at
Pete's Blog; the GitHub page for
the software is at
rufus.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/utilities]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 28, 2025 7:55 pm
Burning an ISO file to a CD or DVD on a Windows 11 System
If you wish to burn a
.iso file to a
CD or a DVD on a Microsoft Windows 11 system, you can do so by taking the
following steps.
-
In the Windows File
Explorer, Right-click on the .iso file, then click on Burn, which appears
above the file list.

-
If the appropriate CD/DVD drive does not appear in the "Disc Burner"
field, select it then click on Burn (check the box first
for "Verify disc after burning", if you wish to have the program
verify that the disc can be read successfully after the iso
file is burned to the disc).
-
When the iso file has successfully been written to disc, you should
see "The disc image has been successfully burned to disc." You can
then click on the Close button.
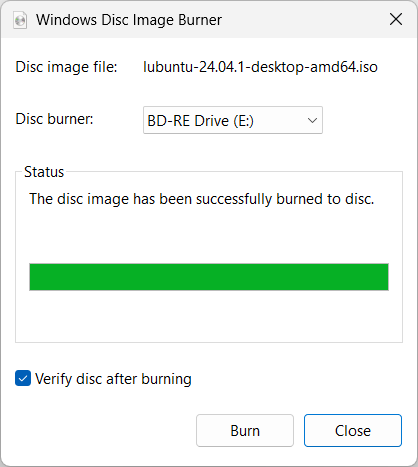
The disc will then be ejected.
[/os/windows/win11]
permanent link
Mon, Jan 27, 2025 10:06 pm
Transferring files over an RDP connection
If you are connected to a remote Microsoft Windows system from another
Windows system via the
Remote Desktop
Protocol (RDP) using the Microsoft terminal services client provided by
Microsoft with its Windows operating systems, mstsc.exe, you can copy and
paste files from one system to the other as you would from one directory
to another on one of the systems. E.g., if I want to copy a file from a
remote Windows 11 system to my local Windows 11 system, I can select it in the
Windows
File Explorer
on the remote system and then switch back to my local system
and go to the directory where I want to place it using the File Explorer
on that system and then hit
Ctrl-V, i.e, the
Ctrl and
V keys, to paste the file into that directory. You can use the same
technique to copy a directory, i.e., you can right click on the directory and
choose "copy" and then switch to the other system and navigate in the File
Explorer to where you wish to copy the directory and then and use the paste
function, e.g.
Ctrl-V to copy
I don't know how well the technique may work on very large files or
directories, e.g., ones that are multiple gigabytes, but I've found it works
well at least for those several megabytes in size. I also have not tested what
happens if you try another copy and paste operation before the first one
has completed.
Related:
-
Transferring Files Via the Remote Desktop
Date: March 13, 2010
[/os/windows/software/remote-control/rdp]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact






