Sun, Oct 29, 2017 10:10 pm
Decoding base64-encoded text in a .eml file with Python
I received an email message from someone that contained an attachment that
had a .eml filename extension. When I viewed that file, I found the
usual email header fields, i.e., "from", "to", "cc",
and "subject", but for the body of the message I saw the following:
Content-Type: multipart/alternative;
boundary="_000_22D42B1E120C59488B6A96BA13E639711E185536NDMSMBX403ndcna_"
MIME-Version: 1.0
--_000_22D42B1E120C59488B6A96BA13E639711E185536NDMSMBX403ndcna_
Content-Type: text/plain; charset="utf-8"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
QXMgZmFyIGFzIG15IGxpbWl0ZWQgdW5kZXJzdGFuZGluZyBvZiB0aGUgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXJzIGdv
<text snipped>
YnNwOzwvbzpwPjwvc3Bhbj48L3A+DQo8L2Rpdj4NCjxwIGNsYXNzPSJNc29Ob3JtYWwiPjxvOnA+
Jm5ic3A7PC9vOnA+PC9wPg0KPC9kaXY+DQo8L2JvZHk+DQo8L2h0bWw+DQo=
--_000_22D42B1E120C59488B6A96BA13E639711E185536NDMSMBX403ndcna_--I needed to decode the base64 encoded text. Fortunately,
Python has a
base64 module that
can be used for that purpose. So I created the following Python script to
decode the encoded portion of the .eml file. The script expects the name of
the input file to be provided on the command line and will print an error
message and terminate if the file name isn't provided. If the filename is
provided, the script will read the file line by line looking for the
"Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64" which indicates that after one following
blank line the encoded text will commence. The output will be displayed on
the screen but can be
redirected to a file.
#!/usr/bin/python
import base64, sys
try:
sys.argv[1]
except IndexError:
print "Error - missing input file name! Usage", sys.argv[0], "infile"
sys.exit(1)
else:
fileName = sys.argv[1]
base64_marker = "Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64"
block_of_lines = ""
with open(fileName) as input_data:
# Skips text before the beginning of the base64 encoded block:
for line in input_data:
if line.strip() == 'Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64':
break
for line in input_data: # Skip blank line
break
# Reads text until the end of the block:
for line in input_data: # Append lines to block_of_lines
block_of_lines = block_of_lines + line
print base64.b64decode(block_of_lines)
[/languages/python]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 28, 2017 10:45 pm
Checking operating system information with WMIC
You can use wmic os get commands on a Microsoft Windows system
to view information related to the operating system via a command-line
interface (CLI). E.g., to determine the version of the operating system you
can issue the command
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC)
command wmic os get version.
C:\Users\Public>wmic os get version
Version
10.0.15063
C:\Users\Public>
Or if you know the system is running a particular version of the Windows
operating system, e.g., Windows 10, but want to see just the build number
for that version of Windows, you could issue the command wmic os get
BuildNumber.
C:\Users\Public>wmic os get BuildNumber
BuildNumber
15063
C:\Users\Public>
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/commands/wmic]
permanent link
Wed, Oct 25, 2017 10:36 pm
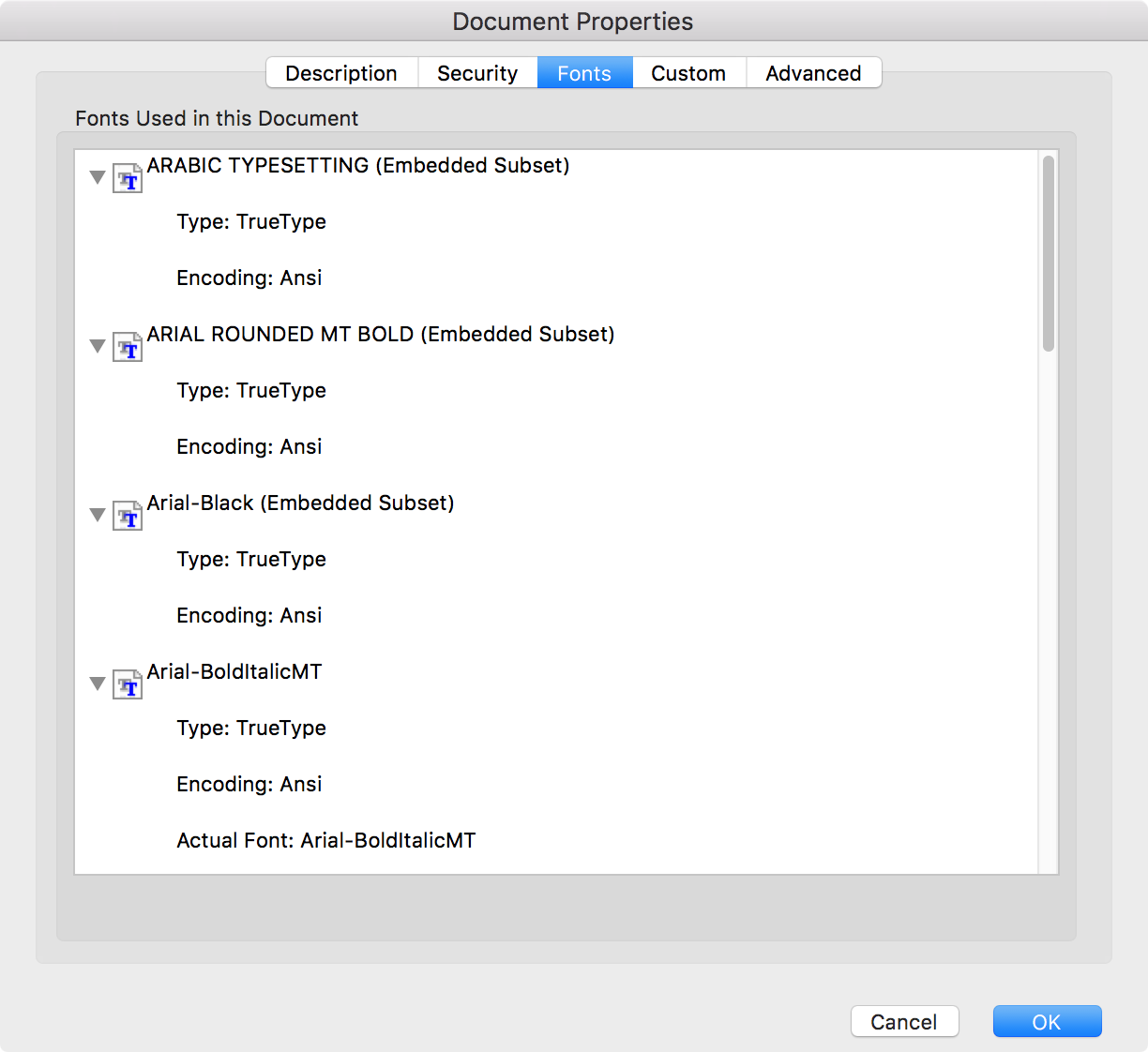
Viewing the fonts used in a PDF document on a Mac OS X system
To view the list of documents contained in a
PDF document with Adobe Acrobat Reader DC on a
Mac OS X
system, with the file open in Acrobat Reader DC, click on File then
select Properties and then click on the Fonts tab.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Sun, Oct 22, 2017 11:09 pm
Text not printing, PowerShell cmdlets not working, etc.
A user reported that when she printed
Microsoft Excel spreadsheets or
QuickBooks
invoices, no text would appear on the printouts. She had reported the
same problem about a month ago. When I rebooted the system then, the problem
went away, but this time rebooting didn't help. After I requested that
she reboot the system, I was told the problem remained, so when I was
able to get to the system to troubleshoot, I first checked to make sure
the system had been rebooted rather than QuickBooks simply being restarted.
It was then that I noticed a lot of other functionality was no longer
available. E.g., when I tried to
use the systeminfo command to find the last reboot time, I saw an error
message instead of the time the system was last rebooted.
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.15063]
(c) 2017 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Users\Pam>systeminfo | find /i "Boot"
Loading Operating System Information ...ERROR: Invalid class
C:\Users\Pam>systeminfo
Loading Operating System Information ...ERROR: Invalid class
C:\Users\Pam>wmic os get lastbootuptime
os - Alias not found.
C:\Users\Pam>
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/win10]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 21, 2017 10:13 pm
Using PowerShell to determine the installed version of Windows
You can determine the version of Microsoft Windows installed on a system
from a
PowerShell prompt using [System.Environment]::OSVersion.Version
or (Get-WmiObject -class Win32_OperatingSystem).Caption.
PS C:\Users\Public> [System.Environment]::OSVersion.Version
Major Minor Build Revision
----- ----- ----- --------
10 0 15063 0
PS C:\Users\Public> (Get-WmiObject -class Win32_OperatingSystem).Caption
Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
PS C:\Users\Public> (Get-WmiObject -class Win32_OperatingSystem)
SystemDirectory : C:\WINDOWS\system32
Organization : Microsoft
BuildNumber : 15063
RegisteredUser : Jeanne
SerialNumber : 00330-80000-00000-AA775
Version : 10.0.15063
PS C:\Users\Public>
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Fri, Oct 20, 2017 10:57 pm
Querying disks with the PowerShell Get-Disk cmdlet
You can use the PowerShell Get-Disk cmdlet to query disk drives
within or attached to a PC running the
Microsoft Windows operating system. E.g.:
PS C:\Users\Public> Get-Disk
Number Friendly Name Serial Number HealthStatus OperationalStatus Total Size Partition
Style
------ ------------- ------------- ------------ ----------------- ---------- ----------
0 ST3320418AS 9VMNNJDN Healthy Online 298.09 GB MBR
4 Generic- C... 058F63626421 Healthy No Media 0 B RAW
6 Generic- M... 058F63626423 Healthy No Media 0 B RAW
3 Generic- S... 058F63626420 Healthy No Media 0 B RAW
5 Generic- S... 058F63626422 Healthy No Media 0 B RAW
1 Lexar USB ... AA58ZF9FJCCALAOA Healthy Online 14.92 GB MBR
2 WD My Pass... WXP1A27034VH Healthy Online 931.48 GB GPT
PS C:\Users\Public>[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 14, 2017 8:59 pm
Text_factory that can support 8-bit bytestrings
I wrote a
Python script that will download a webpage, extract a portion
of the text displayed on the page and write the extracted portion to an
SQLite
database. When I ran the script, I saw the message below displayed:
You must not use 8-bit bytestrings unless you use a text_factory that
can interpret 8-bit bytestrings (like text_factory = str). It is highly
recommended that you instead just switch your application to Unicode
strings.
I had created the following function to establish the connection to the
SQLITE 3 database:
def create_connection (db_file):
""" Create a database connection to an SQL database
Return connection object or none """
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
return conn
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return None[ More Info ]
[/languages/python]
permanent link
Fri, Oct 13, 2017 10:59 pm
Checking the uptime for a Windows system using PowerShell
If you want to determine how long a Microsoft system has been running since
it was last rebooted from a command-line interface (CLI), you can do so using
PowerShell. You can do so by subtracting the last boot time from the current
date and time. The Get-Date cmdlet shows the current date and time
and (Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem).LastBootUpTime shows
the last time the system was booted.
PS C:\Users\public\documents> (Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem).LastBootUpTime
Tuesday, October 10, 2017 9:12:14 PM
PS C:\Users\public\documents> (Get-Date) - (Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem).LastBootUpTime
Days : 3
Hours : 1
Minutes : 29
Seconds : 26
Milliseconds : 717
Ticks : 2645667172021
TotalDays : 3.06211478243171
TotalHours : 73.4907547783611
TotalMinutes : 4409.44528670167
TotalSeconds : 264566.7172021
TotalMilliseconds : 264566717.2021
PS C:\Users\public\documents>
You can use the alias GCIM for Get-CimInstance
to save some typing, if you wish.
PS C:\Users\public\documents> (GCIM Win32_OperatingSystem).LastBootUpTime
Tuesday, October 10, 2017 9:12:14 PM
PS C:\Users\public\documents>
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Wed, Oct 11, 2017 10:20 pm
Error stating Outlook OST file is in use and cannot be accessed
After I rebooted a Windows 10 PC subsequent to a software update on the system,
when I attempted to reopen
Microsoft Outlook 2016, I saw the message below:
Outlook Data File

|
The file C:\Users\jasmith1\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook\john.a.smith@exmple.com.ost is in use and cannot be accessed. Close any
application that is using this file, and then try again. You might need to restart your computer.
|
[ More Info ]
[/network/email/clients/outlook/2016]
permanent link
Tue, Oct 10, 2017 11:31 pm
Wget and curl functionality via PowerShell on a Windows system
If you are accustomed to using the wget or cURL utilities on
Linux or
Mac OS X
to download webpages from a
command-line interface (CLI), there is a
Gnu
utility,
Wget for Windows
, that you can download and use on systems running Microsoft
Windows. Alternatively, you can use the Invoke-WebRequest
cmdlet from a PowerShell prompt, if you have version 3.0 or greater of
PowerShell on the system. You can determine the version of PowerShell on
a system by opening a PowerShell window and typing $psversiontable.
E.g., in the example below from a Windows 10 system, the version of PowerShell
is 5.1.15063.674.
PS C:\Users\public\documents> $psversiontable
Name Value
---- -----
PSVersion 5.1.15063.674
PSEdition Desktop
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0...}
BuildVersion 10.0.15063.674
CLRVersion 4.0.30319.42000
WSManStackVersion 3.0
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.3
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1
PS C:\Users\public\documents>If you have version 3.0 or later, you can use wget or
curl as an alias for the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet,
at least up through version 5.x. E.g., if I want to download the home
page for the website example.com to a file named index.html, I could use
the command wget -OutFile index.html http://example.com
at a PowerShell prompt. Or I could use either of the following commands,
instead:
curl -OutFile index.html http://example.com
Invoke-WebRequest -OutFile index.html http://example.com
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Mon, Oct 09, 2017 11:13 pm
Checking the version of a Dynamic Link Library (DLL) file
You can check version information for a
Dynamic-link
Library (DLL) file, i.e., a file with a .dll
filename extension, or a
executable file, i.e., a .exe file, from a command-line interface (CLI)
on a Microsoft Windows system by using the Get-Item cmdlet. E.g.:
PS C:\> (Get-Item C:\Windows\explorer.exe).VersionInfo
ProductVersion FileVersion FileName
-------------- ----------- --------
10.0.15063.0 10.0.15063.0 ... C:\Windows\explorer.exe
PS C:\>
If you can't see all of the information, i.e., if you see three
dots indicating that not all of the information is displayed, you can
append | format-list to the command to have the output displayed
in list format.
PS C:\> (Get-Item C:\Windows\explorer.exe).VersionInfo | format-list
OriginalFilename : EXPLORER.EXE.MUI
FileDescription : Windows Explorer
ProductName : Microsoft® Windows® Operating System
Comments :
CompanyName : Microsoft Corporation
FileName : C:\Windows\explorer.exe
FileVersion : 10.0.15063.0 (WinBuild.160101.0800)
ProductVersion : 10.0.15063.0
IsDebug : False
IsPatched : False
IsPreRelease : False
IsPrivateBuild : False
IsSpecialBuild : False
Language : English (United States)
LegalCopyright : © Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
LegalTrademarks :
PrivateBuild :
SpecialBuild :
FileVersionRaw : 10.0.15063.608
ProductVersionRaw : 10.0.15063.608
PS C:\>
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
Sun, Oct 08, 2017 10:57 pm
Calculating file checksums on an OS X system
If you need to calculate a
checksum, aka
cryptographic hash value or digital fingerprint, on a
Mac
OS X
system, you can use the
md5
command to calculate a
MD5 checksum, which is equivalent to the
md5sum utility on Linux
systems, and the
shasum
command to calculate Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA). The default value for
shasum, if no
algorithm is specified, is
Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA-1), but you can specify other
algorithms, such as
Secure Hash
Algorithm 2 (SHA-2), e.g. SHA-256, using the
-a option. E.g.
-a 256 for SHA-256.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 07, 2017 10:59 pm
Determining the day of year value using Python
I sometimes need to determine the day of the year corresponding to today's
date. The day of year starts with January 1 as day 1 and for 2017, December
31 is day 365. You can find sites online that will provide those values,
e.g. Day Numbers for 2017
or
NOAA's
DOY
Calendar. Or, on a system with
Python installed, e.g.,
Linux or
OS X, you
can use the
datetime module to obtain the day of the year corresponding to the
current date as shown below:
$ python
Python 2.7.10 (default, Oct 23 2015, 19:19:21)
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 7.0.0 (clang-700.0.59.5)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import datetime
>>> datetime.datetime.today().timetuple().tm_yday
280
>>> exit()
$
Since today is October 7 of the year 2017, the day of the year is 280.
If you want to obtain the day of year (DOY) for another date, you can use
datetime.date(year, month, day).timetuple().tm_yday
where year is the relevant year, month is the month,
and day is the day of interest. E.g., March 1, 2017 is DOY 60:
>>> import datetime
>>> datetime.date(2017, 3, 1).timetuple().tm_yday
60
>>>
[/languages/python]
permanent link
Fri, Oct 06, 2017 11:15 pm
Viewing DHCP information on an OS X system
If you want to determine the IP address of the
DHCP server
from which a Mac
OS X system received its IP address,
subnet
mask, etc., you can obtain that information from a
command-line interface (CLI), i.e., a
Terminal window by using the command ipconfig getpacket
interface where interface is the relevant network
interface, which will usually be en0 or en1.
You can issue the command ifconfig -a in a Terminal
window to see the network interfaces on the system and which have
IP addresses assigned to them.
getpacket interface-name
Prints to standard output the DHCP/BOOTP packet that the
client accepted from the DHCP/BOOTP server. This command is
useful to check what the server provided, and whether the
values are sensible. This command outputs nothing if
DHCP/BOOTP is not active on the interface, or the attempt to
acquire an IP address was unsuccessful.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Sun, Oct 01, 2017 10:53 pm
Finding Gmail SMTP entries in Sendmail log files
I wanted to determine how many connections I was receiving per day from
Gmail
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) servers to my email
server running
Sendmail on a
CentOS Linux system and the IP addresses of the Gmail
servers that were sending email to users on my server. So I created a simple
Python script to search for lines in the maillog file,
/var/log/maillog for any lines containing "relay" and
"google.com" on the same line, since the Gmail servers are in
Google's domain.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact



