Determining the version of a PDF document
If you have a Portable Document
Format (PDF) file and wish to determine the version of the PDF standard
used for the document, that information is stored in the first line of the
file. You can open the file with a
text editor, such
as the Windows
Notepad application on a Microsoft Windows system and view
the first line to determine the PDF version used for the file.
You will see %PDF-x.y where x.y is the
version of the PDF standard used in the creation of the file,
e.g., %PDF-1.7 for version 1.7.
On a Microsoft Windows system, you could also open a
PowerShell window (you can type PowerShell
in the Windows Search field and click on the
application when you see it returned in the list of
results) and use the Get-Content
cmdlet
and the -First parameter followed by the number one.
E.g.:
PS C:\> Get-Content "July 2024 Newsletter.pdf" -First 1
%PDF-1.7
PS C:\>
Related:
-
PowerShell Get-Content equivalents to Linux head and tail commands
Date: March 22, 2024
[/os/windows/PowerShell]
permanent link
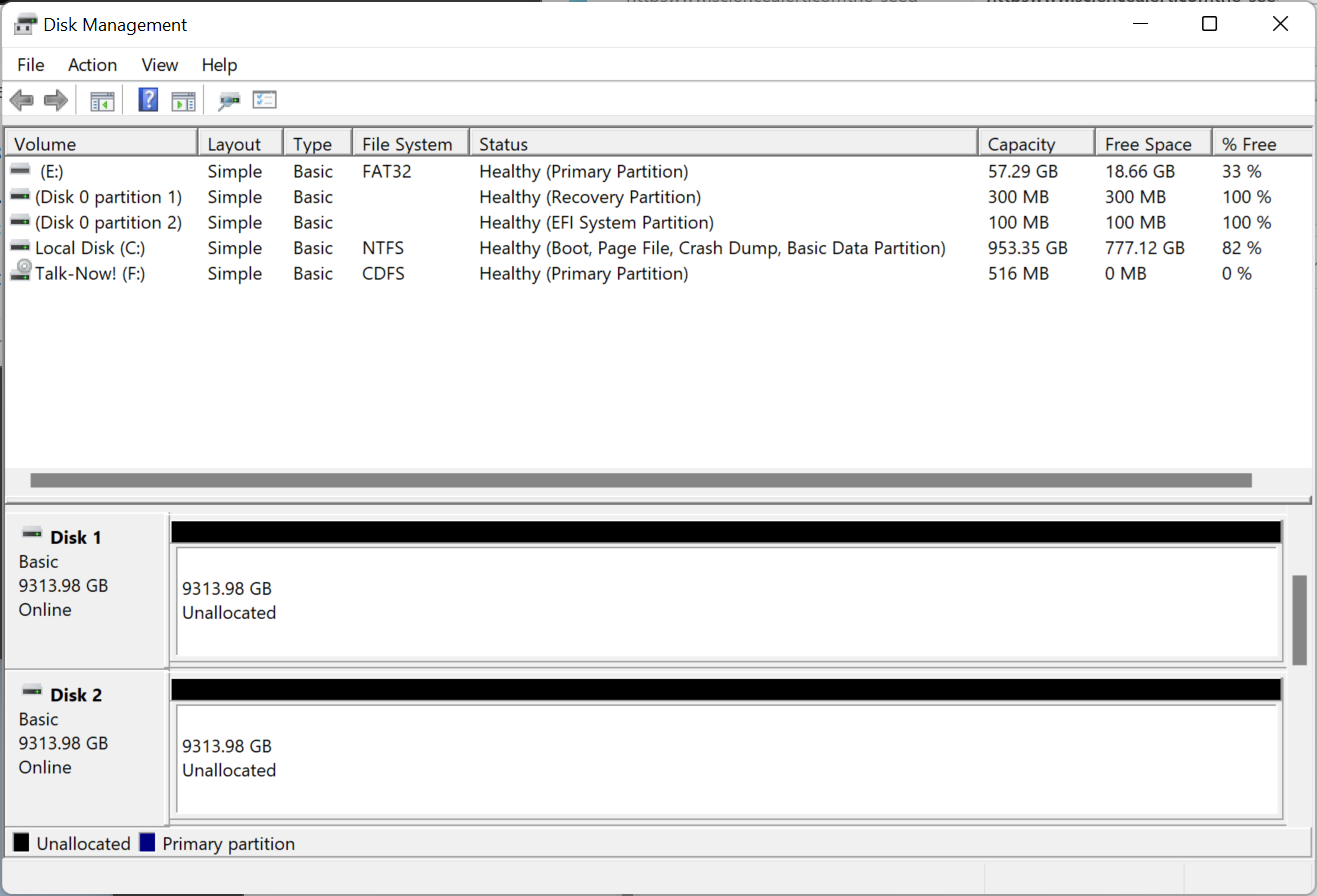
Mirroring Disks with Windows Disk Management
I added two Western
Digital 10 TB hard disk drives to a Windows 11 system.
I wanted to have the second hard disk drive (HDD) mirror the first, which
is a
Redundant Array of Independent Disks 1 (RAID 1) configuration. You
can configure Windows to mirror the drives using the Disk Management utility
that comes with the Microsoft Windows operating system. To run the
utility, you can
open a command prompt with
administrator privileges and then type diskmgmt.msc
and hit Enter. You will then see a window showing all the drives
attached to the system. In this case, the new 10 TB drives are shown as
"unallocated", since they have not been partitioned and formatted yet.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows]
permanent link
Installing OpenSSH server software on an Ubuntu Linux system
To set up an
Ubuntu
Linux system as a
Secure
Shell (SSH) server, you can take the following steps:
- Open a terminal window.
- In the terminal window, issue the command
sudo apt-get install openssh-server.
- Enable and start the ssh server service by
issuing the command
sudo systemctl enable ssh --now.
If you wish to enable the service, but not start it immediately, you
can omit the --now at the end of the command, i.e., you
can use sudo systemctl enable ssh and then later issue
the command sudo systemctl start ssh to start the service.
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/linux/ubuntu]
permanent link
Determining the version of an installed package on an Ubuntu Linux system
If you wish to view information for a
package installed
on an Ubuntu Linux system,
you can use the command apt show packageName or
dpkg -s packageName where packageName is the
name of the relevant package. If you are only interested in the version number
for a package, you can
pipe the output
of either command into the grep
command.
$ apt show net-tools
Package: net-tools
Version: 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5
Priority: optional
Section: net
Origin: Ubuntu
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com>
Original-Maintainer: net-tools Team <team+net-tools@tracker.debian.org>
Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug
Installed-Size: 819 kB
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.34), libselinux1 (>= 3.1~)
Homepage: http://sourceforge.net/projects/net-tools/
Task: ubuntukylin-desktop
Download-Size: 204 kB
APT-Manual-Installed: yes
APT-Sources: http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 Packages
Description: NET-3 networking toolkit
This package includes the important tools for controlling the network
subsystem of the Linux kernel. This includes arp, ifconfig, netstat,
rarp, nameif and route. Additionally, this package contains utilities
relating to particular network hardware types (plipconfig, slattach,
mii-tool) and advanced aspects of IP configuration (iptunnel, ipmaddr).
.
In the upstream package 'hostname' and friends are included. Those are
not installed by this package, since there is a special "hostname*.deb".
$ apt show net-tools | grep "Version:"
WARNING: apt does not have a stable CLI interface. Use with caution in scripts.
Version: 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5
$ dpkg -s net-tools
Package: net-tools
Status: install ok installed
Priority: important
Section: net
Installed-Size: 800
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com>
Architecture: amd64
Multi-Arch: foreign
Version: 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.34), libselinux1 (>= 3.1~)
Description: NET-3 networking toolkit
This package includes the important tools for controlling the network
subsystem of the Linux kernel. This includes arp, ifconfig, netstat,
rarp, nameif and route. Additionally, this package contains utilities
relating to particular network hardware types (plipconfig, slattach,
mii-tool) and advanced aspects of IP configuration (iptunnel, ipmaddr).
.
In the upstream package 'hostname' and friends are included. Those are
not installed by this package, since there is a special "hostname*.deb".
Homepage: http://sourceforge.net/projects/net-tools/
Original-Maintainer: net-tools Team <team+net-tools@tracker.debian.org>
$ dpkg -s net-tools | grep "Version:"
Version: 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5
$
Another command that will show you the installed version of a package
on a Ubuntu systems is apt-cache policy packageName.
$ apt-cache policy net-tools
net-tools:
Installed: 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5
Candidate: 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5
Version table:
*** 1.60+git20181103.0eebece-1ubuntu5 500
500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 Packages
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
$
[/os/unix/linux/ubuntu]
permanent link
Set up Hyper-V on Windows 11
Microsoft provides a capability to create
virtual machines (VMs)
within the Windows
operating system
via Hyper-V. To set up
Microsoft's Hyper-V virtualization software on a Windows 11 system
so that you can create and use virtual machines on the system, you can
type Turn Windows features in the Windows Search field
at the bottom of your screen and thn select the Control Panel option
to "Turn Windows features on or off" when it is displayed.
In the Windows Features window, scroll down until you see Hyper-V. If
you click on the plus sign next to its check box, you will see there are
two subcomponents, Hyper-V Management Tools and Hyper-V Platform.
- Hyper-V Management Tools - Includes GUI and command-line tools for
managing Hyper-V
- Hyper-V Platform - Provides the services that you can use to create and
manage virtual machines and their resources
If you check the Hyper-V check box, the two subcomponents will both be
turned on. Click on OK when you are done. You will then see
"Searching for required files", which should be followed by "Applying
changes" and then the completion window where you will be notified that
"Windows needs to reboot your PC to finish installing the requested
changes." Click on the Restart now button to immediately apply the
changes or you can click on Don't restart to apply them at a later
reboot of the system.
[ More Info ]
[/software/virtualization/Hyper-V]
permanent link


