Sat, Oct 31, 2015 10:53 pm
Driverquery
The driverquery command can be used on Microsoft Windows systems to obtain
information on the
device drivers in use on the system. You can use
driverquery /si
to determine which drivers on the system have been digitally
signed and the
/v option to obtain detailed, i.e., verbose,
output for the drivers on the system. You can use the command
wmic loadorder to obtain information on the load order for
the drivers.
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/commands]
permanent link
Tue, Oct 27, 2015 10:07 pm
Installing iperf on CentOS
Iperf is a tool that can
be used to determine the network bandwidth available between two end points.
On one system you run iperf in server mode and on the other you run it in
client mode. On both hosts iperf will report the available bandwidth. E.g.,
below is the output from a system running iperf in server mode:
[root@localhost install]# [ 4] local 192.168.18.44 port 5001 connected with 172.25.2.72 port 55990
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.4 sec 3.00 MBytes 2.42 Mbits/sec
To install Iperf on a CentOS system with yum install iperf,
you may need to configure the system to use the Extra Packages for Enterprise
Linux (EPEL) repository, which you can do by issuing the command
yum install epel-release. A repository is a source for software
packages that can be installed with yum.
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/linux/centos]
permanent link
Mon, Oct 26, 2015 8:36 pm
Downloading a web page with Python
To download a webpage with a
Python script, you can use the following, substituting the URL for the
page you wish to download for the one for which you wish to download the
source code:
import urllib2
url="http://www.example.com/somepage.html"
page =urllib2.urlopen(url)
source=page.read()
print source
If you wish the script to prompt for the URL and a location for a file
where the source code for the web page will be stored, you can use the
following:
import urllib2
url=raw_input("URL: ")
outfile=raw_input("Output file: ")
page =urllib2.urlopen(url)
source=page.read()
f=open(outfile, 'w')
f.write(source)
f.close()The "w" in the f=open(outfile, 'w') line indicates the file
should be opened for writing. Other possible modes for the file are listed
below:
| Modes | Description |
|---|
| r |
Opens a file for reading only. The file pointer is placed at the beginning of the file. This is the default mode. |
| rb |
Opens a file for reading only in binary format. The file pointer is placed at the beginning of the file. This is the default mode. |
| r+ |
Opens a file for both reading and writing. The file pointer placed
at the beginning of the file. |
| rb+ |
Opens a file for both reading and writing in binary format. The file
pointer placed at the beginning of the file. |
| w |
Opens a file for writing only. Overwrites the file if the file
exists. If the file does not exist, creates a new file for writing. |
| wb |
Opens a file for writing only in binary format. Overwrites the file
if the file exists. If the file does not exist, creates a new file for
writing. |
| w+ |
Opens a file for both writing and reading. Overwrites the existing
file if the file exists. If the file does not exist, creates a new file
for reading and writing. |
| wb+ |
Opens a file for both writing and reading in binary
format. Overwrites the existing file if the file exists. If the file
does not exist, creates a new file for reading and writing. |
| a |
Opens a file for appending. The file pointer is at the end of the
file if the file exists. That is, the file is in the append mode. If
the file does not exist, it creates a new file for writing. |
| ab |
Opens a file for appending in binary format. The file pointer is at
the end of the file if the file exists. That is, the file is in the append
mode. If the file does not exist, it creates a new file for writing. |
| a+ |
Opens a file for both appending and reading. The file pointer is at
the end of the file if the file exists. The file opens in the append
mode. If the file does not exist, it creates a new file for reading
and writing. |
| ab+ |
Opens a file for both appending and reading in binary format. The
file pointer is at the end of the file if the file exists. The file
opens in the append mode. If the file does not exist, it creates a new
file for reading and writing. |
If you named the script
download_webpage.py, you could run it from a command line inteface,
aka shell prompt, as follows:
$ python download_webpage.py
URL: http://www.example.com/somepage.html
Output file: example-somepage.html
References:
-
Python Files I/O
tutorialspoint - The largest
Tutorials Library on the web
[/languages/python]
permanent link
Thu, Oct 22, 2015 10:42 pm
Mirroring a display to an external monitor and obtaining information on it under OS X
To mirror what is displayed on a laptop's screen to an external monitor under
Apple's OS X operating system, take the following steps after connecting the
external monitor:
-
Click on the Apple icon on the upper, left-hand of the screen and select
System Preferences.
-
Under Hardware, click on Displays.
-
Click on the Arrangement tab for the display and check the check box
next to Mirror Displays.
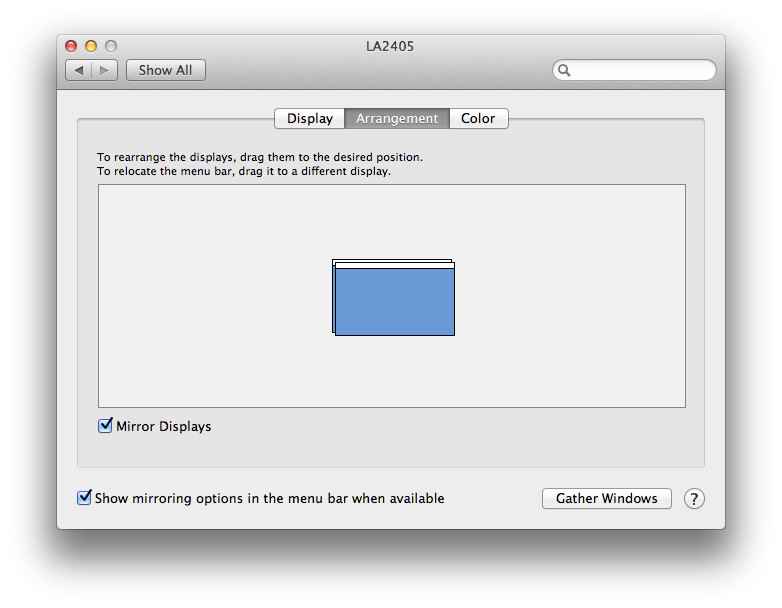
You should then see a copy of the information displayed on the laptop's builtin
monitor also displayed on the external monitor.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Tue, Oct 20, 2015 8:32 pm
Synching Google Drive from the command line
If you want to synchronize files stored on a computer with the Google Drive
cloud from the command line, the only way to do so currently using the
application provided by Google appears to be to kill the
googledrivesync.exe process that handles the synchronization
and then restart it. You can kill the processes - there are actually two
of them running with the same "googledrivesync.exe" name - from the command line
with
taskkill /f /fi "imagename eq googledrivesync.exe" and
then restart them with the command
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Drive\googledrivesync, assuming
that the
googledrivesync application is stored in the
default location of
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Drive\.
[ More Info ]
[/network/web/services/google/drive]
permanent link
Sun, Oct 18, 2015 9:00 pm
Stop Access from rounding number
For a field in an Access 2013 database that I wanted to hold the amperage
for a device's power adapter, e.g., 1.5, I specified the field should
be a number with a "fixed" format. But whenever I put in 1.5, Access would
change it to 2. I clicked on the button to increase the number of
decimal points, but Access would round the number 1.5 to 2.0 then.
To resolve the problem, I clicked on
View for the table and
selected
Design View.
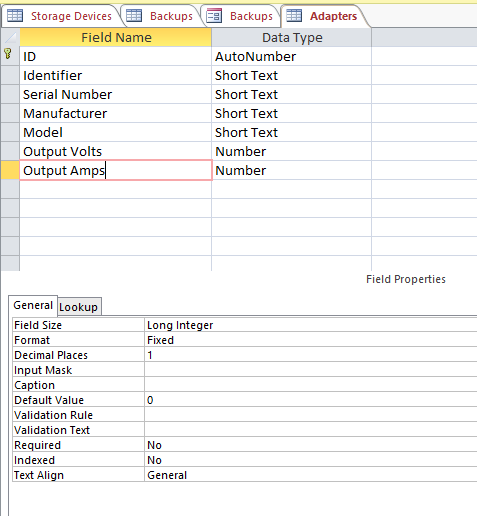
I could then see, when I selected the field that was to hold the amperage,
that the Field Size value was set to Long Integer. An
integer field, obviously, won't hold a fractional part for the number.
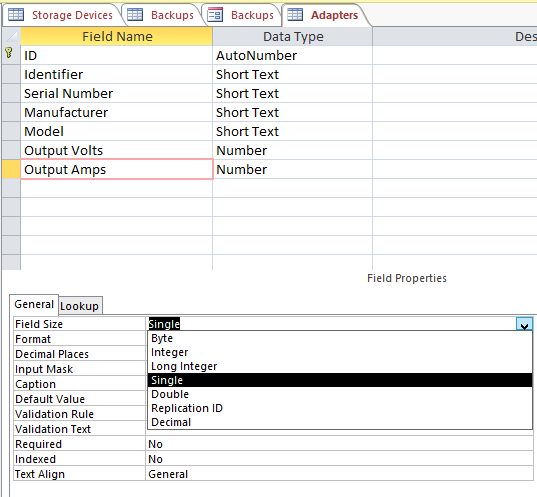
I set the value to Single instead by clicking in the
field and selecting that option from the dropdown list, so I could store
a floating point value in the field rather than an integer.
From the dropdown list for field size, you can select the following
values:
Setting | Description |
Decimal precision | Storage size |
Byte |
Stores numbers from 0 to 255 (no fractions). |
None |
1 byte |
Decimal |
Stores numbers from -10^38-1 through 10^38-1 (.adp)
Stores numbers from -10^28-1 through 10^28-1 (.mdb, .accdb) |
28 |
2 bytes |
Integer |
Stores numbers from -32,768 to 32,767 (no fractions). |
None |
2 bytes |
Long Integer |
(Default) Stores numbers from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 (no
fractions). |
None |
4 bytes |
Single |
Stores numbers from
-3.402823E38 to -1.401298E&45
for negative values and from
1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 for positive values. |
7 |
4 bytes |
Double |
Stores numbers from
-1.79769313486231E308 to
-4.94065645841247E-324
for negative values and from
4.94065645841247E-324 to
1.79769313486231E308 for positive values. |
15 | 8 bytes |
Replication ID |
Globally unique identifier (GUID) |
N/A |
16 bytes |
Note: you can see the values that each one can hold by hitting
the F1 key to get online help on the topic after clicking
on the value stored in the Field Size field while in
Design View.
When I switched back to Datasheet View by clicking on
View and then selecting Datasheet View, I was then
able to change the value from 2.0 to 1.5 and have it remain as 1.5, i.e.,
Access had stopped rounding numbers to the nearest integer for the field.
References:
-
Field Size Property
[/software/database/access]
permanent link
Tue, Oct 13, 2015 9:35 pm
Obtaining the model number and serial number for a HDD from the command line
If you wish to obtain the model number and serial number for a hard disk drive
(HDD) from the command line on a Microsoft Windows system, you can use
the
Windows Management Instrumentation command line tool
wmic at a
command prompt or
get-wmiobject -class win32_diskdrive from a
Windows PowerShell
prompt.
For wmic, you can use the following command:
C:\Users\JDoe\Documents>wmic diskdrive get caption, model, serialnumber
Caption Model SerialNumber
TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 73RISBDFS
Seagate Backup+ Desk USB Device Seagate Backup+ Desk USB Device NA5J4H3R
In the above example, I also included the caption
parameter to get a description for the drive that may help me more
easily identify it, though in this case the caption information and the
model information are the same. In the above case, the Toshiba drive
is the internal drive in the system while the Seagate is an external,
USB-attached drive.
To use PowerShell to obtain the same information, I could use the
command below:
PS C:\Users\JDoe> get-wmiobject -class win32_diskdrive | format-table Caption, Model, SerialNumber
Caption Model SerialNumber
------- ----- ------------
TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 73RISBDFS
Seagate Backup+ Desk USB Device Seagate Backup+ Desk USB Device NA5J4H3R
You can obtain much more information on drives in PowerShell with the
get-wmiobject -class win32_diskdrive | format-list * command.
If the drive supports
Self-Monitoring, Analysis
and Reporting Technology (SMART), you can use the status
command to learn if the drive may be failing or is encountering problems that
could lead to a drive failue.
PS C:\Users\Jim> get-wmiobject -class win32_diskdrive | format-table Caption, Model, Status, SerialNumber
Caption Model Status SerialNumber
------- ----- ------ ------------
TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 Pred Fail 73RISBDFS
Seagate Backup+ Desk USB D... Seagate Backup+ Desk USB D... OK NA5J4H3R
The Toshiba drive has a status of Pred Fail, which indicates
a SMART-enabled hard disk may be functioning correctly, but a failure is
predicted soon. You can also retrieve the status of a drive using
the wmic command.
C:\Users\JDoe\Documents>wmic diskdrive get model, status, serialnumber
Model SerialNumber Status
TOSHIBA MQ01ABD075 73RISBDFS Pred Fail
Seagate Backup+ Desk USB Device NA5J4H3R OK
Other parameters you can use with wmic to obtain drive information, such
as the capacity of the drive, etc., are listed at
Using wmic to get disk drive
information.
A PowerShell command that can be used to determine which drive
the operating system considers to be drive zero, drive one, etc. is shown
below:
PS C:\Users\JDoe> Get-WmiObject Win32_PhysicalMedia | Format-Table Tag, SerialNumber
Tag SerialNumber
--- ------------
\\.\PHYSICALDRIVE0 73RISBDFS
\\.\PHYSICALDRIVE1 NA5J4H3R
\\.\CDROM1
\\.\CDROM0
References:
-
Physical disk status is not OK
Microsoft Developer Network
-
Disk Drive Dangers - SMART and WMI
I Programmer - programming, reviews
and projects
-
Using wmic to get disk drive
information
Date: July 10, 2010
MoonPoint Support
[/os/windows/commands/wmic]
permanent link
Mon, Oct 12, 2015 12:13 pm
MediaMonkey taking a long time to start playing music
My wife told me that
MediaMonkey (MM) on her PC was taking a long time to start
playing songs; it could take 20 seconds to begin playing a song after
she double-clicked on it from the Windows Explorer to play the song. She
showed the problem to me by having Windows 8 use Media Monkey as the default
player for MP3 files. When she clicked on a song, I observed it did take as
long as she reported, but when she then switched the default player to
Windows Media Player, songs started playing almost immediately when she
double-clicked on them. I checked the version of MediaMonkey on her system
and found it was 4.1.7.1741. When I checked the MediaMonkey website at
MediaMonkey >> Download,
I found the current version is 4.1.9.1764. After I downloaded and installed
that version, the problem no longer occurred.
[/os/windows/software/audio-video/MM]
permanent link
Sun, Oct 11, 2015 5:54 pm
Adding or creating a K-Meleon Macro Module (KMM)
The open source
K-Meleon
web browser has its own macro language which can be used to extend the
capabilities of the browser. Macros are stored in K-Meleon Macro Module (KMM)
files, which can be placed in the
macros directory beneath
the direcory where you installed K-Meleon to make them available to all users
of the browser on a system; K-Meleon runs on Microsoft Windows systems.
There are many .kmm files available for download in the
K-Meleon Macro Library
. Instructions for adding a KMM to a system are at
K-Meleon - Adding a Macro
Module. Instructions for creating macros are at
K-Meleon - Creating a
Macro Module.
[/network/web/browser/k-meleon]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 10, 2015 4:06 pm
ACDSee Video Converter Pro - Error opening file for writing
When I attempted to install
ACDSee Video Converter Pro 4.1 on my wife's computer, I received
the mesage "Error opening file for writing" referencing the file
CheckWinVer.exe.
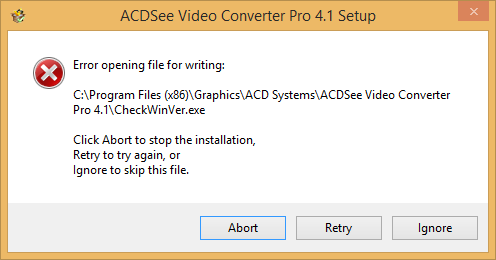
The problem was due to the fact that I hadn't right-clicked on the
installation file and chosen "Run as administrator". When I aborted the
installation and started over running it as administrator, the program
installed successfully.
[/software/audio_video]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 10, 2015 3:48 pm
Clearing Media Monkey and Windows Media Player Libraries
If you wish to clear the Windows Media Player (WMP) library, but not delete
the music from your system, within the program while viewing your music,
hit
Ctrl-A to select all entries then right-click and select
Delete. When a window opens prompting you as to whether you wish
to delete items only from your library or wish to also delete the music
files, e.g., MP3 files, from your system, leave "Delete from library only"
selected and click on
OK.
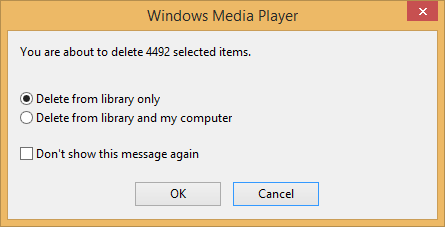
In
MediaMonkey,
to clear the database, you can click on File then select Clear
Database. You will then be prompted to type "YES" to ensure that
you didn't inadvertently select to remove all entries from the Media
Monkey music library for your account. For a family member who wanted
to reinitialize her library, though, I found that after typing "YES"
in all capital letters to proceed that a blue circling ring appeared
for awhile, but afterwards all of the entries remained visible in the
proram. If I clicked on File and selected Close or clicked
on the "X" at the upper, right-hand corner of the Media Monkey window,
the program would not close. When I closed the program through the
Windows Task Manager, reopening it showed all the entries remained.
Perhaps, because she had such an extensive music collection, the
program may have been taking a long time to clear the database, but
the library was never cleared after we performed several attempts
to clear it. But there is another way to clear the database and
start fresh. You can, instead, delete the Media Monkey database
file, MM.DB. After killing the program through the Task
Manager, I deleted that file, which, on a Windows 8 system is found at
C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\MediaMonkey\MM.DB
where username is the username for the account. Note: you may
have to turn on the display of hidden files, folders, and drives through
the Windows Explorer in order to view that location. I also deleted
MM.DB-journal, which is found at that location. Then,
when she reopened Media Monkey, the library was empty and she was able
to add the music she wanted in the library back into it.
[/os/windows/software/audio-video]
permanent link
Sat, Oct 03, 2015 7:15 pm
Controlling the volume on a Microsoft Windows system from the command line
To control the sound volume on a Microsoft Windows system, e.g., Windows 7
or 8, you can run the
sndvol command from a command prompt.
If you issue the command with no options, it will open the
Volume Mixer
that will allow you to adjust the audio volume.
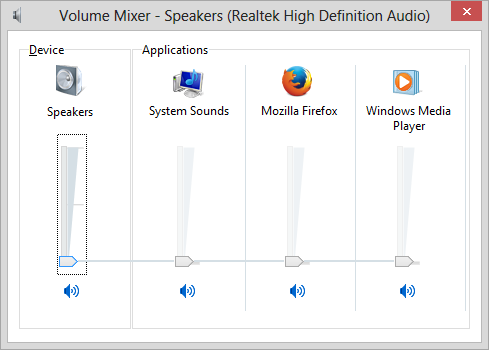
You can view just the master volume slider if you use the -f
option, i.e., sndvol -f.
You can add an additional numeric parameter to the command line to
control the horizontal and vertical position of the mixer window, if you
wish, as explained at
Windows 7 - Open the Volume Control popup from the command prompt.
[/os/windows/commands]
permanent link
Fri, Oct 02, 2015 10:41 pm
Sending Encrypted Email with the OS X Mail Application
The
Mail application found on Mac OS X systems supports the
transmission and decoding of encrypted email that uses public key
unfrastructure (PKI) certificates. You will see an open padlock icon on
messages that will be sent unencrypted. If you have a public certificate
for a recipient, you can click on the button with that symbol on it to
encrypt the message.
OS X also provides the command line security utility for managing
certificates. You can use security find-certificate email_address
where email_address is the email address to which you wish to
send email to determine if you already have a public certificate for the
recipient in your keychain.
If you are using PKI software from Entrust on the system, you can also
use it to retrieve public certificates for recipients.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact










