Tue, Feb 27, 2018 11:10 pm
Error message "You don't have permission to access / on this server."
I had been running an Apache webserver under
OS X El Capitan on my
MacBook
Pro laptop. After an upgrade on the laptop, now running
OS X El Capitan (10.11.6), when I tried accessing the site
via http://localhost, I saw a page with the title "403 Forbidden"
and the following text displayed on the page:
Forbidden
You don't have permission to access /
on this server.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x/apache]
permanent link
Mon, Feb 26, 2018 11:46 pm
Outlook reports a security problem with an encryption certificate
When I attempted to send a
PKI-encrypted email message to several recipients
from Microsoft Outlook for Mac 2016 (version 15.41),
I saw the message "Encryption certificates for some recipients could
not be found in the Outlook Contacts. Do you want to search the
Active Directory servers for them?"
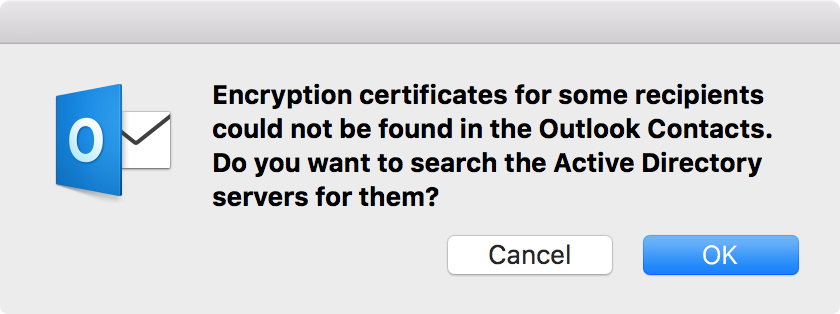
I clicked on OK and then saw the message "The following recipients
have encryption certificates with security problems. Do you still want to
send this encrypted message?"
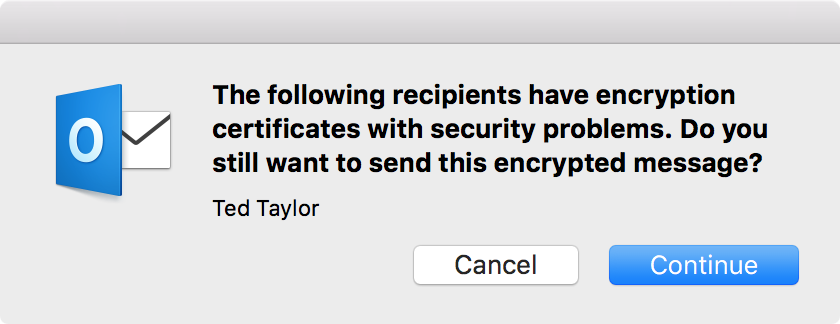
I clicked on Cancel and checked on whether Outlook was storing a
public key certificate for the person in my contacts list. He
was in the contact list, but there was no certificate associated
with the person in the contacts list when I clicked on the
Certificates tab.
[ More Info ]
[/network/email/clients/outlook]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 24, 2018 10:51 pm
Installing gnuplot and using it for a simple graph
Gnuplot
is a command-line interface (CLI) program that can be used to
create two and three-dimensional plots on a variety of operating systems
including
Linux, OS
X/macOS,
Unix, and Microsoft Windows systems. If you use
CentOS Linux,
you can install it with the
yum package management utility with yum install
gnuplot. The information shown below is for the gnuplot 4.6.2 package
on a CentOS system.
$ rpm -qi gnuplot
Name : gnuplot
Version : 4.6.2
Release : 3.el7
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: Fri 23 Feb 2018 09:30:00 PM EST
Group : Applications/Engineering
Size : 1551543
License : gnuplot and MIT
Signature : RSA/SHA256, Thu 03 Jul 2014 09:41:15 PM EDT, Key ID 24c6a8a7f4a80eb5
Source RPM : gnuplot-4.6.2-3.el7.src.rpm
Build Date : Tue 10 Jun 2014 12:07:58 AM EDT
Build Host : worker1.bsys.centos.org
Relocations : (not relocatable)
Packager : CentOS BuildSystem <http://bugs.centos.org>
Vendor : CentOS
URL : http://www.gnuplot.info/
Summary : A program for plotting mathematical expressions and data
Description :
Gnuplot is a command-line driven, interactive function plotting
program especially suited for scientific data representation. Gnuplot
can be used to plot functions and data points in both two and three
dimensions and in many different formats.
Install gnuplot if you need a graphics package for scientific data
representation.
$
Once you've installed the software on a Linux system, you can start
the program by typing gnuplot and hitting Enter. You
will get a gnuplot prompt where you can type commands, e.g., help
for information on using the program. You can terminate the program by typing
exit at the prompt.
[ More Info ]
[/software/graph/gnuplot]
permanent link
Thu, Feb 22, 2018 11:01 pm
Installing GIMP on OS X
To install the
GNU Image Manipulation Program
(GIMP) on
OS X systems, take the following steps:
-
Download the GIMP installation file from
GIMP - Downloads. The
file is an Apple Disk Image .dmg file.
-
Double-click on the downloaded file to start the installation process.
-
When the GIMP installation window opens, you will see "GIMP.app" in the
window that opens. Click on "GIMP.app" and drag it over into a
Finder window with the Applications folder
displayed to complete the installation of the GIMP application into that folder.
[ More Info ]
[/os/os-x]
permanent link
Mon, Feb 19, 2018 11:24 pm
xlrd and hidden worksheets
I use the xlrd
module in Python scripts to extract data from Excel workbooks. You can
use the Python xlrd module to
list the worksheets in a workbook and you can use the
xlrd.sheet "visibility" value to determine whether a sheet is hidden and,
if it is hidden, whether a user can unhide the sheet. The value should be
either 0, 1, or 2 with the numbers having the following meaning:
Visibility of the sheet:
0 = visible
1 = hidden (can be unhidden by user -- Format -> Sheet -> Unhide)
2 = "very hidden" (can be unhidden only by VBA macro)
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python/excel]
permanent link
Sun, Feb 18, 2018 10:10 pm
Displaying a tooltip
A tooltip, aka infotip or hint, is a small box of text
that appears when a user hovers the mouse pointer over an item, such as a
particular word or phrase, on a webpage. If you wish to display a
tooltip when a user hovers the mouse pointer over text on a webpage,
there are a number of ways you can do so. The simplest way to do so
is to specify a title attribute, which is an
HTML global attribute with the
span tag. E.g.:
<span title="This is the tooltip text to be displayed when the mouse is
hovered over the spanned text.">example text</span>
This is an example using the above technique with example text.
[ More Info ]
[/network/web/html]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 17, 2018 1:43 pm
Windows 10 Blue Screen - Page Fault in Nonpaged Area
When we awoke this morning, my wife found a blue screen displayed on her
PC running Windows 10 Professional with the message "Your PC ran into a
problem and needs to restart. We'll restart for you." and "Stop Code: PAGE
FAULT in NONPAGED AREA". She tried rebooting the system several
times and powering the system off and on, but the message kept
reappearing. I rebooted the system and hit the F8 key before Windows
started - you may have to reboot several times to hit the key right before
Windows starts to have it take effect. That took me to a Recovery window
where I saw the message
It looks like
Windows didn't load correctly. If you'd like to restart and try
again, choose "Restart my PC" below. Otherwise, choose "See advanced
repair options" for troubleshooting tools and advanced options.
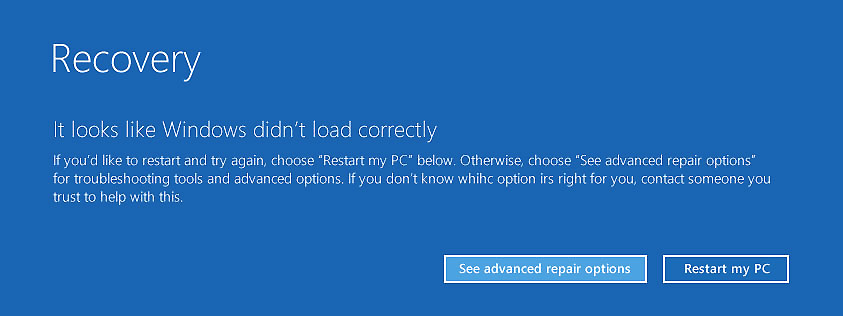
[ More Info ]
[/os/windows/win10]
permanent link
Thu, Feb 15, 2018 10:22 pm
Enabling the Developer Tab in Excel for Mac 2016
To be able to view the Developer Tab in
Microsoft Excel for Mac 2016, take the following steps:
-
Click on Excel at the top, left-hand corner of the Excel window and
the select Preferences.
-
On the Excel Preferences window, click on View in the
Authoring section.
-
In the View window, click on the check box next to Developer tab,
which you will see in the In Ribbon, Show section.
-
You can close that window by clicking on the "x" in the red circle at the
top, left-hand corner of the window. You should then see Developer
as a selectable option to the right of Data, Review, and View on the menu
bar at the top of the Excel window.
-
If you click on the Developer tab, you should see options that
include Visual Basic, Macros, Record Macro, Add-ins, Excel Add-ins, Button,
Group Box, Combo Box, Label, Check Box, Scroll Bar, List Box, Option Button,
and Spinner.
[ More Info ]
[/software/office/excel]
permanent link
Wed, Feb 14, 2018 9:31 pm
Extracting embedded Microsoft Office files from an Excel spreadsheet
I work with Excel workbooks on my
MacBook Pro
laptop that have embedded
PowerPoint
slides on some worksheets. The workbooks, which I need to review, are
created by others. When I review them, I
extract information from
the Excel workbooks to an SQLite database with Python and also have begun
extracting information embedded by
Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) into files as
noted in Extracting the
contents of a directory in a zipfile using Python. Some of the
embedded files are PowerPoint files, but when they are extracted they
have a .bin extension, which I can't open in
PowerPoint without changing the
filename extension from .bin to .ppt. To automate the renaming process,
I created a Python script, extract_embedded.py that will extract
the embedded information to files in an "embedded" directory beneath the
current working directory and then rename any .bin files that are PowerPoint
files to have a .ppt extension. The script is shown below.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python/excel]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 10, 2018 10:55 pm
Extracting the contents of a directory in a zipfile using Python
A Microsoft Excel file with an .xlsx or .xlsm
filename extension is an
Office
Open XML (OpenXML) zipped, XML-based file. The OpenXML format was developed by Microsoft for
spreadsheets, charts, presentations and word processing documents. If you
change the file extension to .zip by renaming the file, you can
extract the contents of the zip file as you would with any other
zip file - see Zipping
and unzipping Excel xlsx files. Excel workbooks can contain other documents
embedded within them using
Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) technology - see
Using olefile to
obtain metadata from an OLE CDF V2 file. I often need to extract an
embedded PowerPoint slide or
Visio
diagram from Excel .xlsm files, so I've been renaming the files to
zip files and unzipping them as I would other zip files, but, since
I want to automate the process and extract just specific embedded
files for further processing within a Python script, I created the
script below to extract the embedded files, which are contained
within a xl/embeddings subdirectory within the .xlsm
zip files. The script uses the
zipfile module
to deal with the zip files.
Python's
OS module is used to check for the existence of the destination
directory and create it, if it doesn't yet exist.
#!/usr/bin/python
import os, zipfile
dirToExtract = "xl/embeddings/"
destinationDir = "embedded"
infile = raw_input("Enter zipfile: ")
archive = zipfile.ZipFile(infile)
if not os.path.exists(destinationDir):
os.makedirs(destinationDir)
for file in archive.namelist():
if file.startswith(dirToExtract):
archive.extract(file, destinationDir)The script prompts for the file to be unzipped and then extracts just
the "xl/embeddings" folder and the files contained within it to a new
directory it will create within the current working directory. The new
directory will be named "embedded". After extracting the contents of the
"xl/embeddings" directory to the newly created "embedded" folder, I had the
the files below in the case of the particular .xlsm file I used for this
example.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python/excel]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 09, 2018 10:04 pm
Using the Python xlrd module to list the worksheets in a workbook
To view the list of sheets in an
Excel
spreadsheet, I can use the
xlrd module within the
Python script below to obtain the list of
worksheets within the workbook.
#!/usr/bin/python
import xlrd as xl
file_name = raw_input("File: ")
workbook = xl.open_workbook(file_name)
print workbook.sheet_names()If I use the script to display the list of worksheets in a workbook
named report.xlsx that has three sheets named alpha,
beta, and gamma, I would see the following output:
$ ./sheetlist.py
File: report.xlsx
[u'alpha', u'beta', u'gamma']
$
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python/excel]
permanent link
Sun, Feb 04, 2018 11:03 pm
Run a cronjob at the end of every year
At the end of every year, I need to create some new directories to hold
log files with the directory name reflecting the new year on a
CentOS
Linux system. To create those directories on the last day of the year,
December 31, I can use the cron utility found on Linux/Unix and OS X/MacOS systems
to schedule a cronjob to run on the last day of the year. I can edit the
crontab file
that holds jobs to be run at a scheduled time or times by issuing the
crontab command
crontab -e, which will allow me to edit the file with the
vi editor.
If the vi editor is the default editor, which it likely is, but you
are unfamiliar with that editor, you can change the editor for the current
login session to the GNU nano text editor, which may be easier to use for
someone unfamiliar with the vi text editor, by issuing the following command at
the command line.
export EDITOR="/usr/bin/nano"
The value will be reset when you log off or you can reset it manually
with the command below:
export EDITOR="/usr/bin/vi"
I can put the following line in the crontab file to run my script named
end-of-year-dirs at 7:00 AM on December 31 of every year. When
you add a new entry, be sure to hit the Enter key at the end of the
line.
0 7 31 DEC * /home/jdoe/scripts/end-of-year-dirs
[ More Info ]
[/os/unix/commands]
permanent link
Sat, Feb 03, 2018 10:34 pm
Using PyInstaller to create an executable file from a Python script
If you wish to convert Python scripts to executable files that you can run on
systems where Python or all of the needed dependencies for the script are
not installed, one program that is available for
Linux, Mac OS X,
Solaris, AIX, or
Microsoft Windows systems is
PyInstaller. If you have the
pip package manager installed, you can install PyInstaller by running the
command below from the root account.
To then create an executable file that will run on other sytems with that
same operating system, e.g., you can create an executable file on one Linux
system that will run on another Linux system or create an .exe file on a
Microsoft Windows system that can be ported to another Windos system, you can
issue the command pyinstaller yourprogram.py.
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python]
permanent link
Fri, Feb 02, 2018 11:16 pm
Extracting information from a .msg file with Python
I received a
.msg file attachment to an email message I received with
Microsoft Outlook for Mac, which is part of
Microsoft Office 2016 on my
MacBook Pro
laptop. When I double-clicked on the attachment in Outlook to view
the contents of the file, I saw "There is no application specified to open
the document Re_ Netbond.msg."
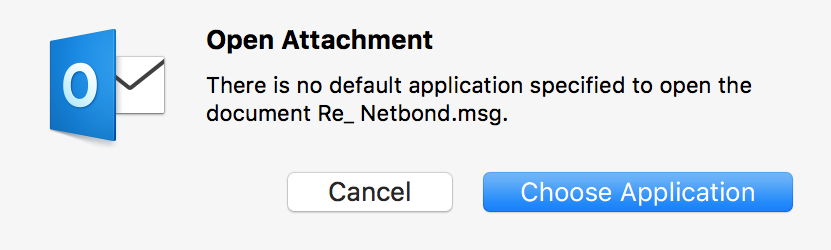
And also a window giving me an option to "Search App Store" with the message
"Search the App Store for an application that can open this document, or
choose an existing application on your computer."
[ More Info ]
[/languages/python]
permanent link

Privacy Policy
Contact






